Setup¶
Setting up a masternode requires a basic understanding of Linux and blockchain technology, as well as an ability to follow instructions closely. It also requires regular maintenance and careful security, particularly if you are not storing your Dash on a hardware wallet. There are some decisions to be made along the way, and optional extra steps to take for increased security.
Commercial masternode hosting services are available if you prefer to delegate day-to-day operation of your masternode to a professional operator. When using these hosting services, you retain full control of the 1000 DASH collateral and pay an agreed percentage of your reward to the operator. It is also possible to delegate your voting keys to a representative, see the governance documentation for more information.
Before you begin¶
This guide assumes you are setting up a single masternode for the first time. If you are updating a masternode, see here instead. If Spork 15 is not yet enabled, it is not possible to directly set up a DIP003 masternode. You will need to set up the masternode following the old process and then work through the upgrade procedure. You will need:
- 1000 Dash
- A wallet to store your Dash, preferably a hardware wallet, although Dash Core wallet is also supported
- A Linux server, preferably a Virtual Private Server (VPS)
Dash 0.13.0 implements DIP003, which introduces several changes to how a Dash masternode is set up and operated. A list of available documentation appears below:
- DIP003 Deterministic Masternode Lists
- DIP003 Masternode Changes
- Dash 0.13 Upgrade Information
- Dash 0.13 Upgrade Procedure for Masternodes
- Full masternode setup guide (you are here)
- Information for users of hosted masternodes
- Information for operators of hosted masternodes
It is highly recommended to first read at least the list of changes
before continuing in order to familiarize yourself with the new concepts
in DIP003. This documentation describes the commands as if they were
entered in the Dash Core GUI by opening the console from Tools > Debug
console, but the same result can be achieved on a masternode by
entering the same commands and adding the prefix
~/.dashcore/dash-cli to each command.
Set up your VPS¶
A VPS, more commonly known as a cloud server, is fully functional installation of an operating system (usually Linux) operating within a virtual machine. The virtual machine allows the VPS provider to run multiple systems on one physical server, making it more efficient and much cheaper than having a single operating system running on the “bare metal” of each server. A VPS is ideal for hosting a Dash masternode because they typically offer guaranteed uptime, redundancy in the case of hardware failure and a static IP address that is required to ensure you remain in the masternode payment queue. While running a masternode from home on a desktop computer is technically possible, it will most likely not work reliably because most ISPs allocate dynamic IP addresses to home users.
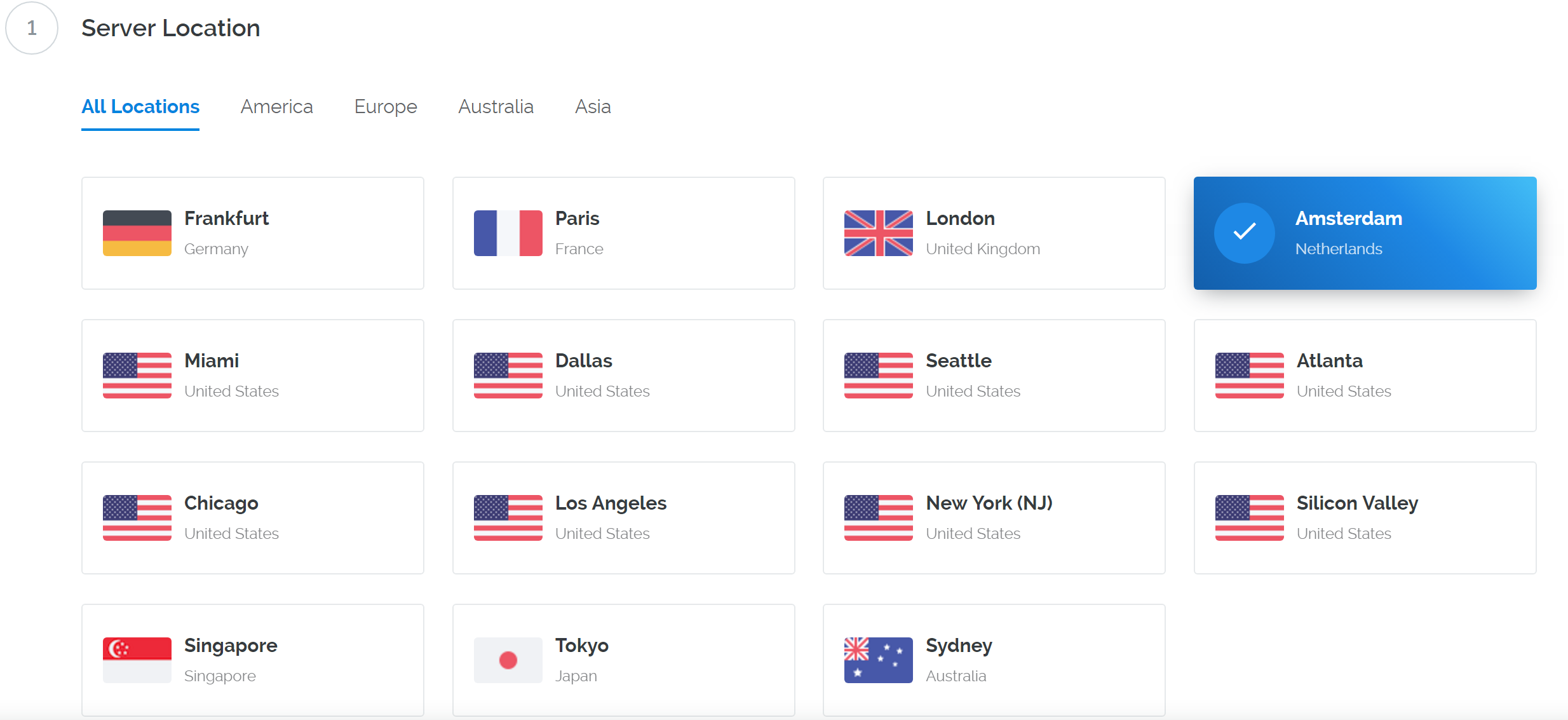
We will use Vultr hosting as an example of a VPS, although DigitalOcean, Amazon EC2, Google Cloud, Choopa and OVH are also popular choices. First create an account and add credit. Then go to the Servers menu item on the left and click + to add a new server. Select a location for your new server on the following screen:
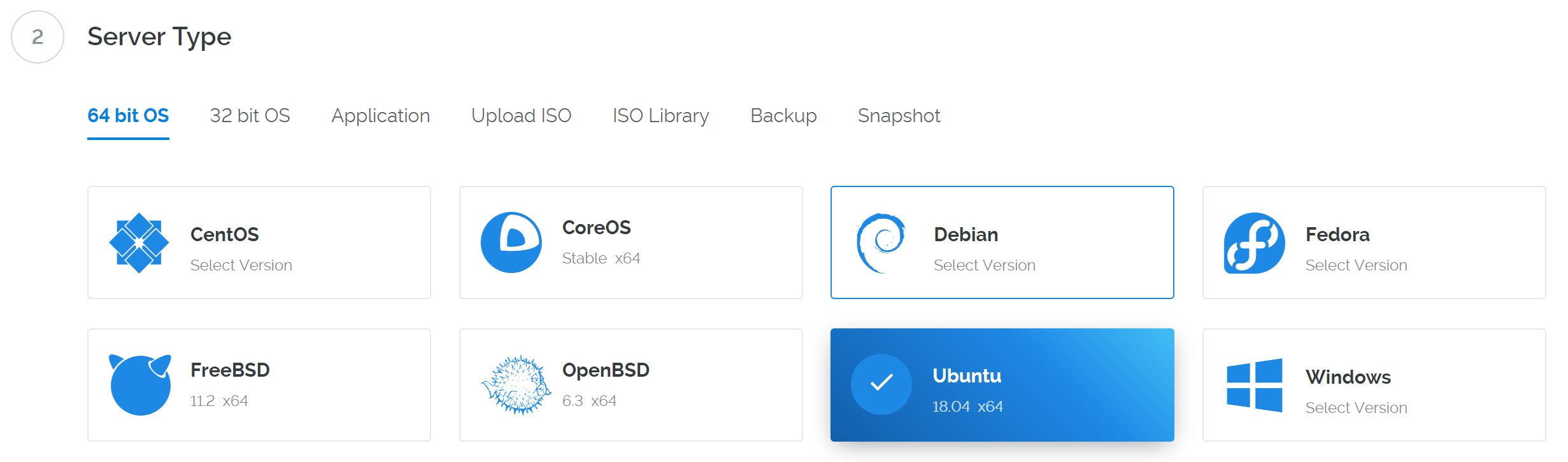
Select Ubuntu 18.04 x64 as the server type. We use this LTS release of Ubuntu instead of the latest version because LTS releases are supported with security updates for 5 years, instead of the usual 9 months.
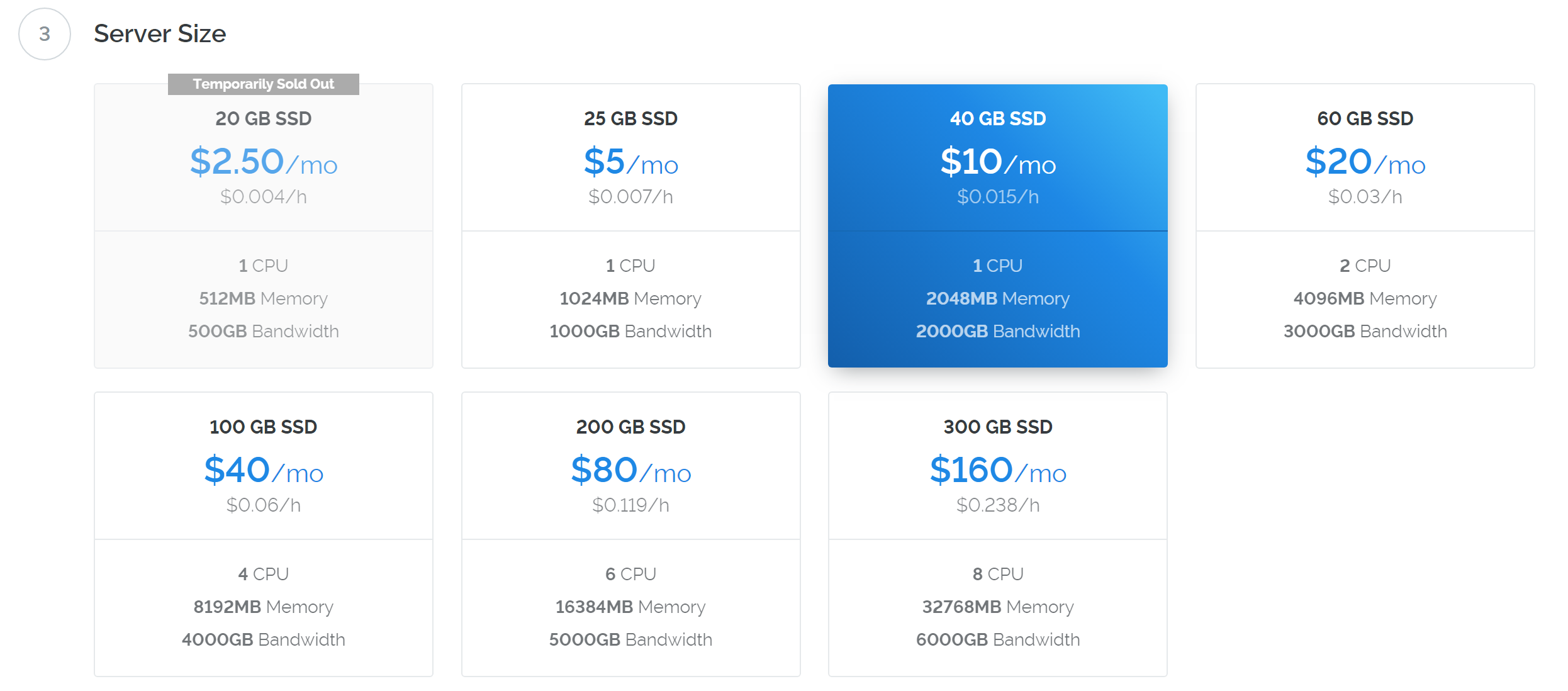
Select a server size offering at least 2GB of memory.
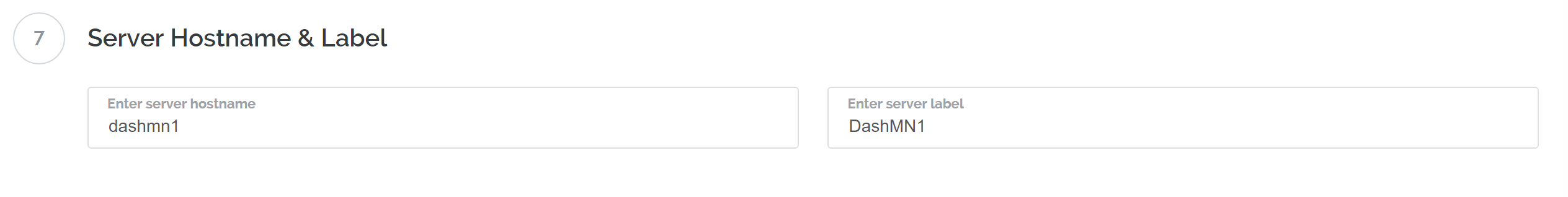
Enter a hostname and label for your server. In this example we will use
dashmn1 as the hostname.
Vultr will now install your server. This process may take a few minutes.
Click Manage when installation is complete and take note of the IP address, username and password.
Set up your operating system¶
We will begin by connecting to your newly provisioned server. On
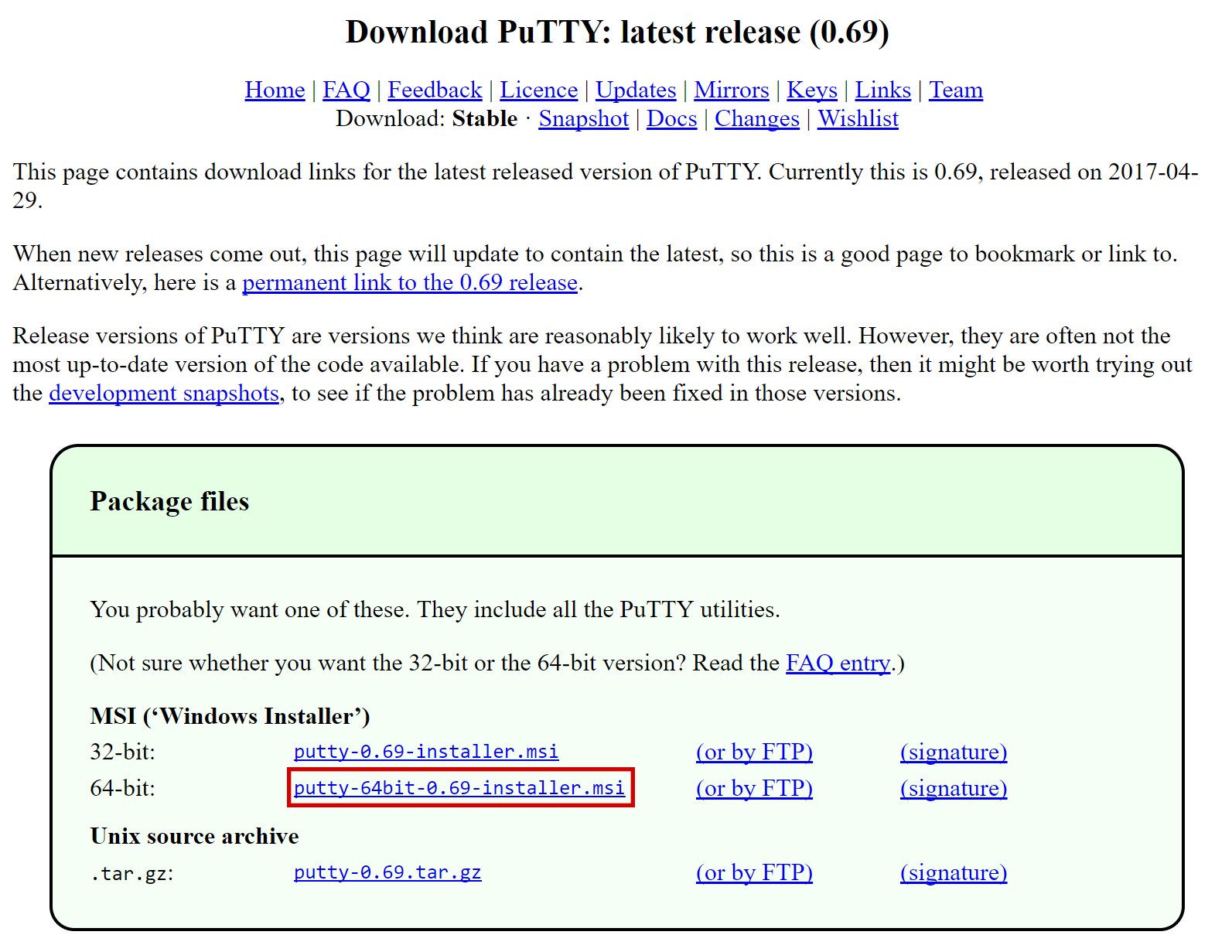
Windows, we will first download an app called PuTTY to connect to the
server. Go to the PuTTY download page
and select the appropriate MSI installer for your system.
On Mac or Linux you can ssh directly from
the terminal - simply type ssh root@<server_ip> and enter your
password when prompted.
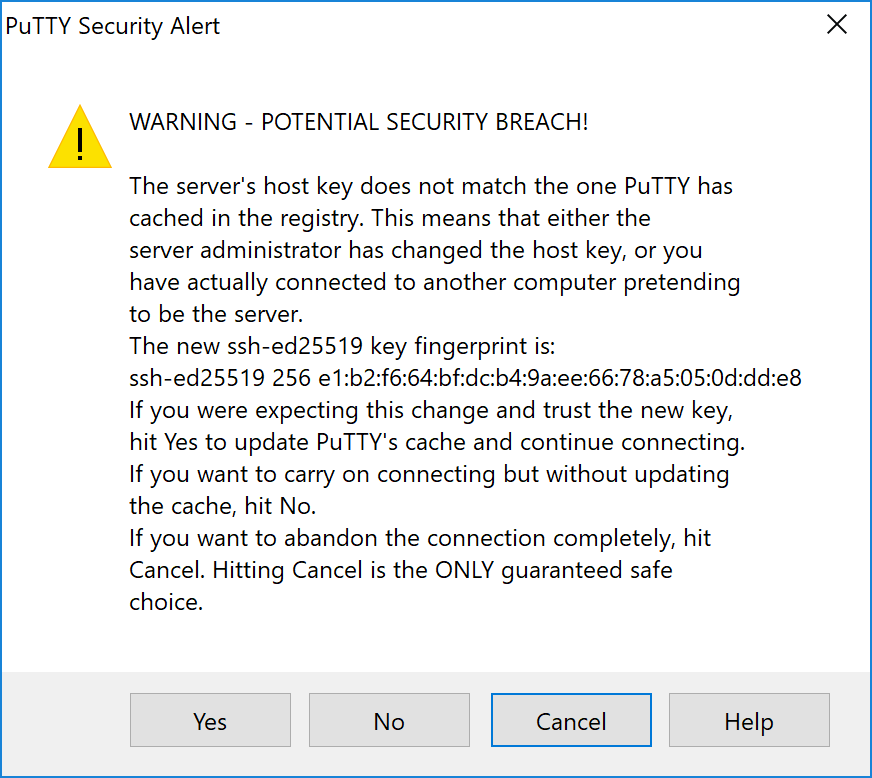
Double-click the downloaded file to install PuTTY, then run the app from your Start menu. Enter the IP address of the server in the Host Name field and click Open. You may see a certificate warning, since this is the first time you are connecting to this server. You can safely click Yes to trust this server in the future.
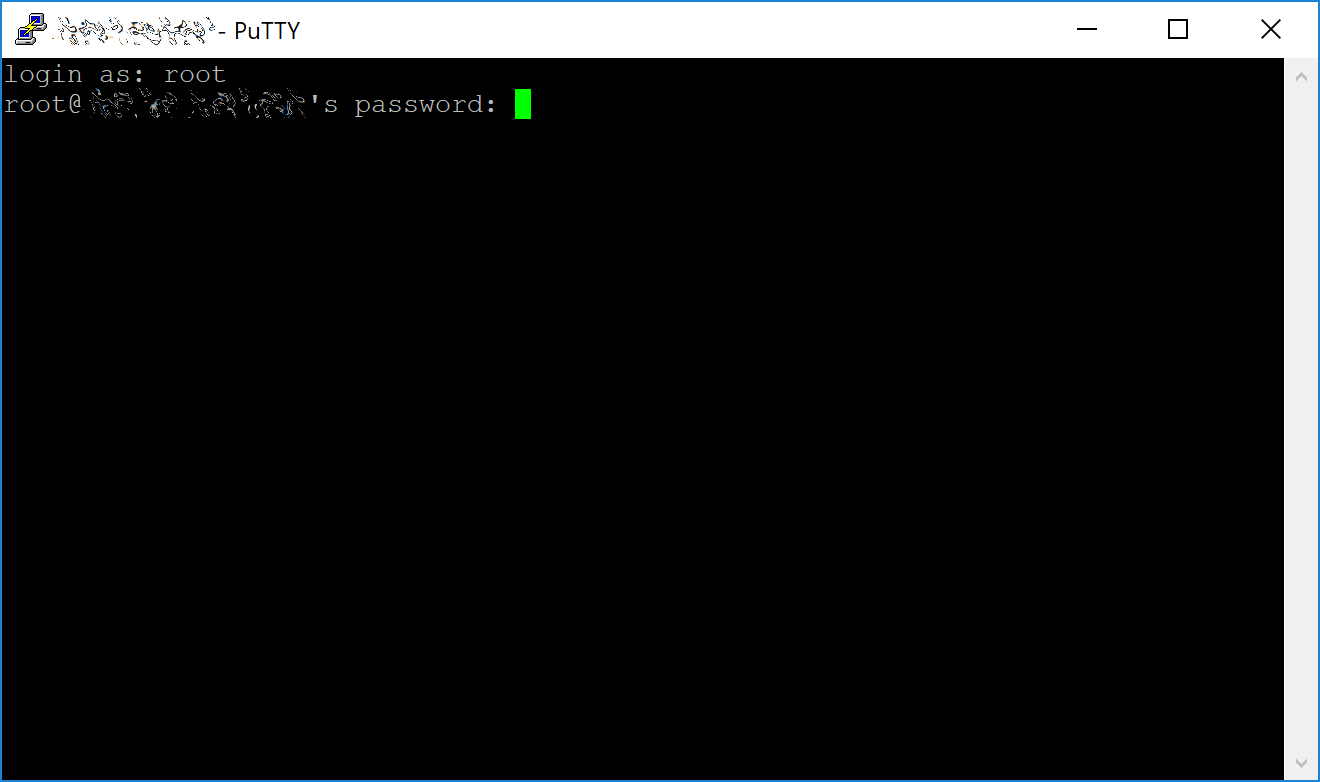
You are now connected to your server and should see a terminal
window. Begin by logging in to your server with the user root and
password supplied by your hosting provider.
You should immediately change the root password and store it in a safe place for security. You can copy and paste any of the following commands by selecting them in your browser, pressing Ctrl + C, then switching to the PuTTY window and right-clicking in the window. The text will paste at the current cursor location:
passwd root
Enter and confirm a new password (preferably long and randomly
generated). Next we will create a new user with the following command,
replacing <username> with a username of your choice:
adduser <username>
You will be prompted for a password. Enter and confirm using a new password (different to your root password) and store it in a safe place. You will also see prompts for user information, but this can be left blank. Once the user has been created, we will add them to the sudo group so they can perform commands as root:
usermod -aG sudo <username>
Now, while still as root, we will update the system from the Ubuntu package repository:
apt update
apt upgrade
The system will show a list of upgradable packages. Press Y and Enter to install the packages. We will now install a firewall (and some other packages we will use later), add swap memory and reboot the server to apply any necessary kernel updates, and then login to our newly secured environment as the new user:
apt install ufw python virtualenv git unzip pv
(press Y and Enter to confirm)
ufw allow ssh/tcp
ufw limit ssh/tcp
ufw allow 9999/tcp
ufw logging on
ufw enable
(press Y and Enter to confirm)
fallocate -l 4G /swapfile
chmod 600 /swapfile
mkswap /swapfile
swapon /swapfile
nano /etc/fstab
Add the following line at the end of the file (press tab to separate each word/number), then press Ctrl + X to close the editor, then Y and Enter save the file.
/swapfile none swap sw 0 0
Finally, in order to prevent brute force password hacking attacks, we will install fail2ban and disable root login over ssh. These steps are optional, but highly recommended. Start with fail2ban:
apt install fail2ban
Create a new configuration file:
nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
And paste in the following configuration:
[sshd]
enabled = true
port = 22
filter = sshd
logpath = /var/log/auth.log
maxretry = 3
Then press Ctrl + X to close the editor, then Y and Enter save the file. Retart and enable the fail2ban service:
systemctl restart fail2ban
systemctl enable fail2ban
Next, open the SSH configuration file to disable root login over SSH:
nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Locate the line that reads PermitRootLogin yes and set it to
PermitRootLogin no. Directly below this, add a line which reads
AllowUsers <username>, replacing <username> with the username
you selected above. Then press Ctrl + X to close the editor, then
Y and Enter save the file.
Then reboot the server:
reboot now
PuTTY will disconnect when the server reboots.
While this setup includes basic steps to protect your server against attacks, much more can be done. In particular, authenticating with a public key instead of a username/password combination and enabling automatic security updates is advisable. More tips are available here. However, since the masternode does not actually store the keys to any Dash, these steps are considered beyond the scope of this guide.
Send the collateral¶
A Dash address with a single unspent transaction output (UTXO) of exactly 1000 DASH is required to operate a masternode. Once it has been sent, various keys regarding the transaction must be extracted for later entry in a configuration file and registration transaction as proof to write the configuration to the blockchain so the masternode can be included in the deterministic list. A masternode can be started from a hardware wallet or the official Dash Core wallet, although a hardware wallet is highly recommended to enhance security and protect yourself against hacking. This guide will describe the steps for both hardware wallets and Dash Core.
Option 1: Sending from a hardware wallet¶
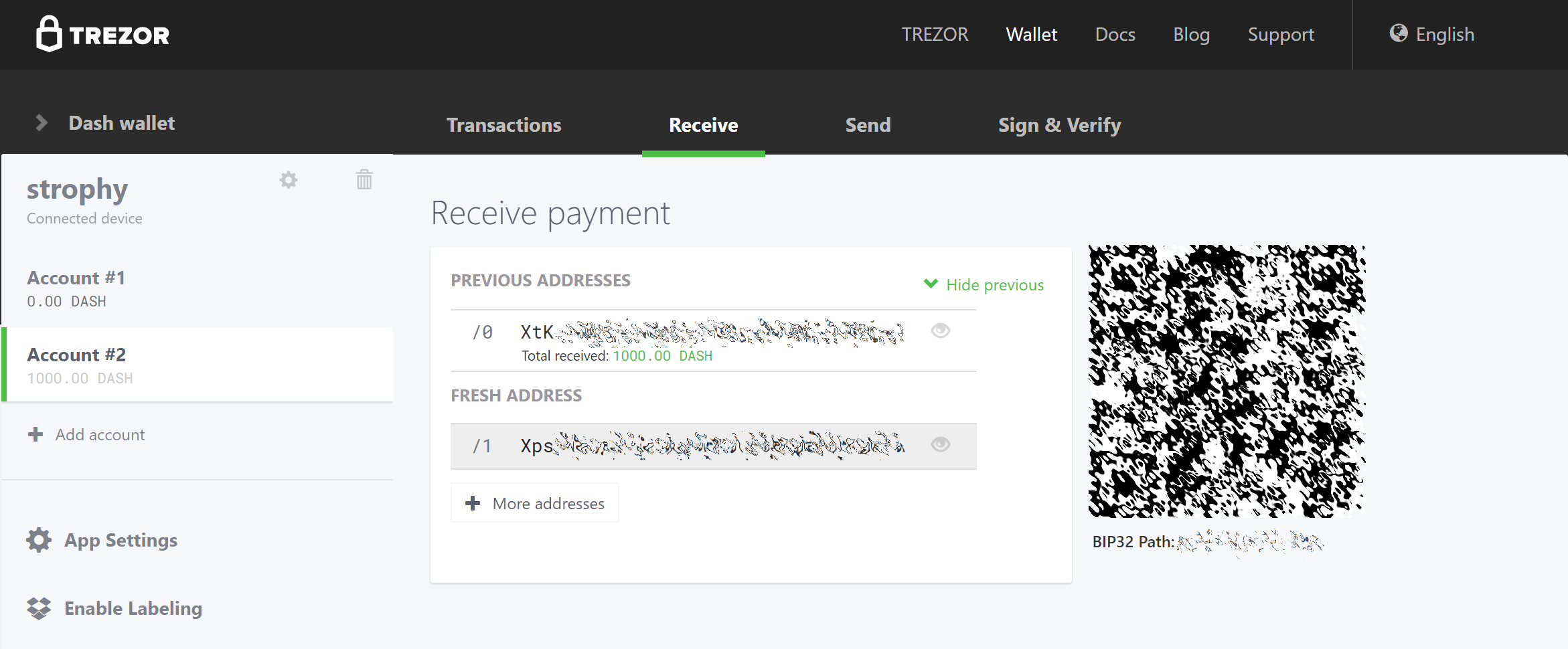
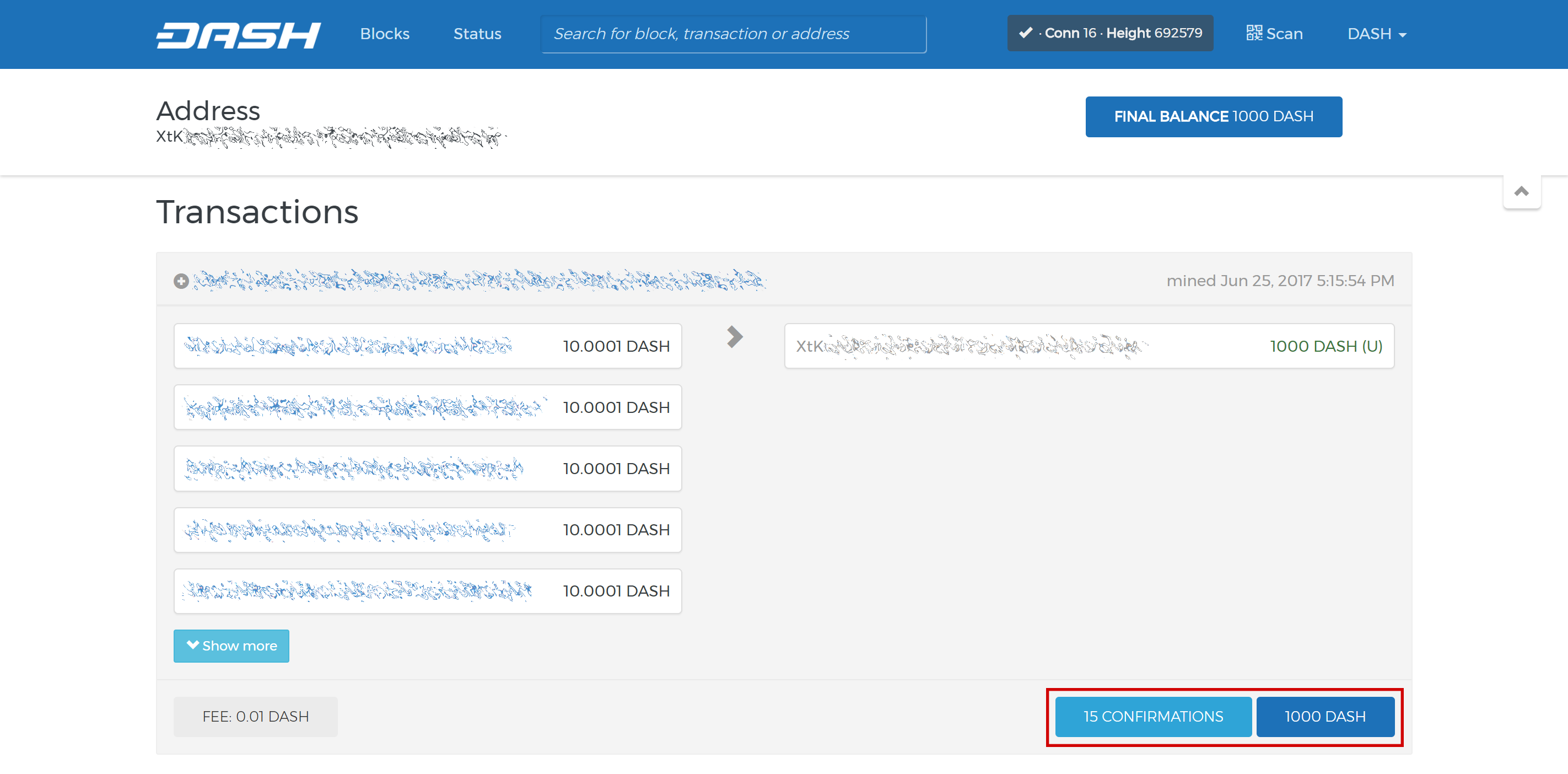
Set up your Trezor using the Trezor wallet at https://wallet.trezor.io/ and send a test transaction to verify that it is working properly. For help on this, see this guide - you may also choose to (carefully!) add a passphrase to your Trezor to further protect your collateral. Create a new account in your Trezor wallet by clicking Add account. Then click the Receive tab and send exactly 1000 DASH to the address displayed. If you are setting up multiple masternodes, send 1000 DASH to consecutive addresses within the same new account. You should see the transaction as soon as the first confirmation arrives, usually within a few minutes.
Once the transaction appears, click the QR code on the right to view the transaction on the blockchain. Keep this window open as we complete the following steps, since we will soon need to confirm that 15 confirmations exist, as shown in the following screenshot.
While we are waiting for 15 confirmations, download the latest version of the Dash Masternode Tool (DMT) from the GitHub releases page here. Unzip and run the file. The following window appears.
Click the third button from the left Check Dash Network Connection in the top left corner of the main window to verify that the connection is working. Then connect your Trezor device and click the next button Test Hardware Wallet Connection to verify the Trezor connection is working.
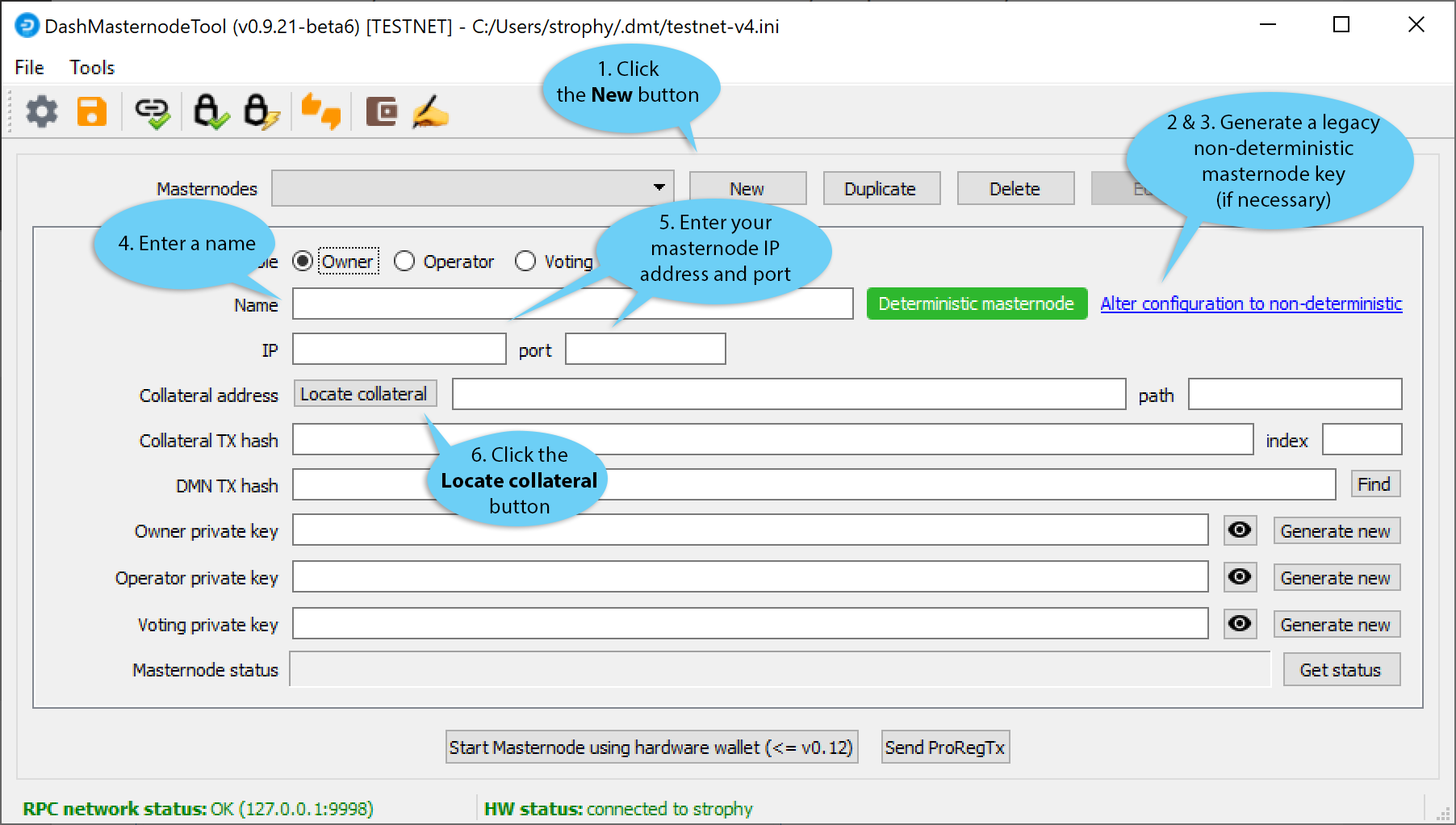
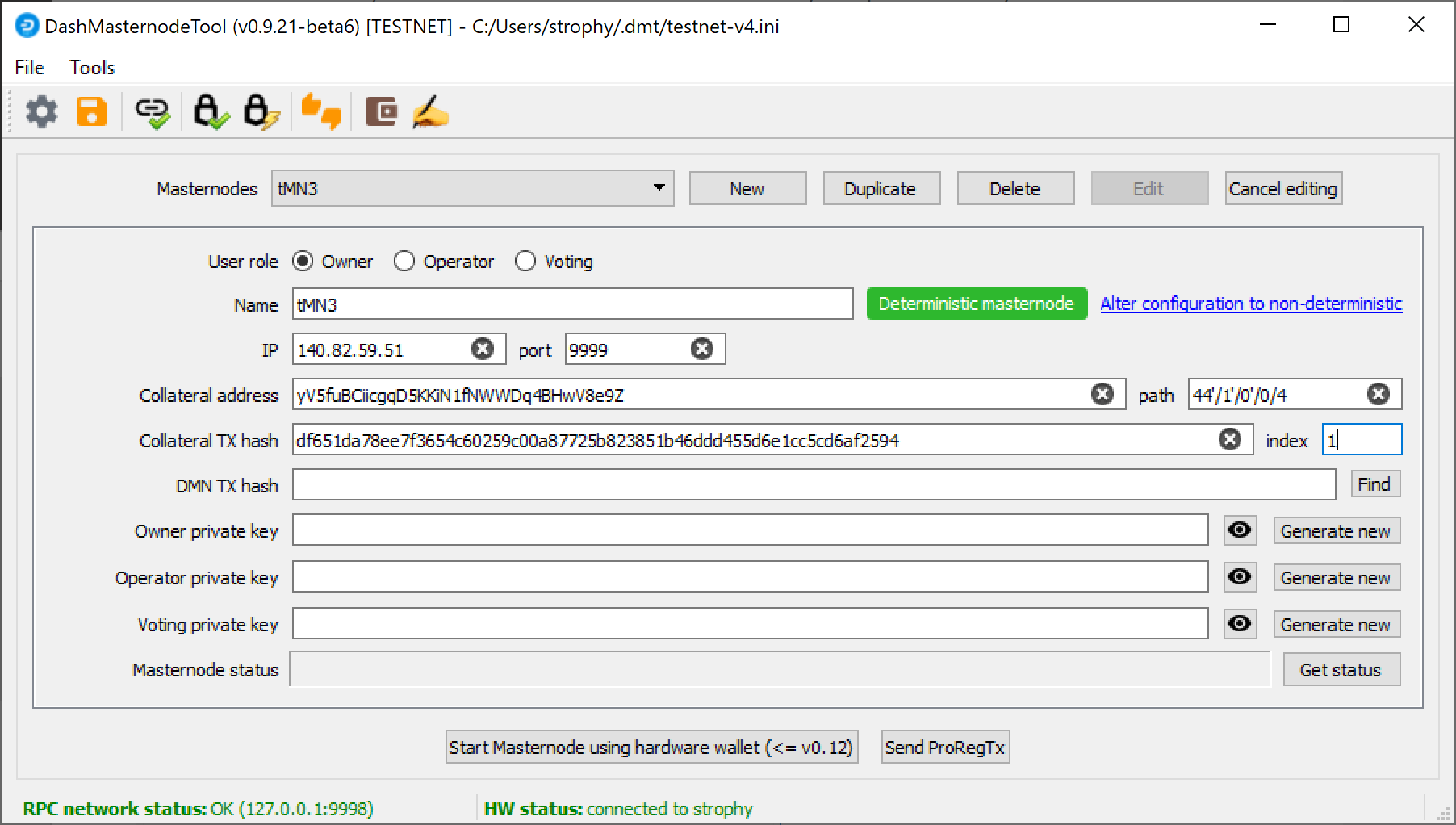
We will now use DMT to extract the transaction ID and legacy masternode key (necessary for successful startup during the DIP003 transition period). Carry out the following sequence of steps as shown in this screenshot:
- Click the New button.
- Ensure you are on the settings page for a Non-deterministic masternode and click Generate new to generate a legacy masternode key. Copy this key into a text editor.
- Click Alter configuration to deterministic
- Enter a name for your masternode. The host name you specified for your VPS above is a good choice.
- Enter the IP address of your masternode. This was given to you by the VPS provider when you set up the server.
- Enter the TCP port number. This should be 9999.
- Click Locate collateral to view unused collateral funding transactions available on the connected hardware wallet. The Collateral address, index and Collateral TX hash fields should be filled automatically
Leave DMT open and continue with the next step: installing Dash Core on your VPS.
Option 2: Sending from Dash Core wallet¶
Open Dash Core wallet and wait for it to synchronize with the network. It should look like this when ready:
Click Tools > Debug console to open the console. Type the following two commands into the console to generate a legacy masternode key (necessary for successful startup during the DIP003 transition period) and a new Dash address for the collateral:
masternode genkey
93PAqQsDjcVdYJHRfQPjsSt5338GCswMnUaSxoCD8J6fiLk4NHL
getnewaddress
yiFfzbwiN9oneftd7cEfr3kQLRwQ4kp7ue
Take note of the legacy masternode private key and collateral address, since we will need it later. The next step is to secure your wallet (if you have not already done so). First, encrypt the wallet by selecting Settings > Encrypt wallet. You should use a strong, new password that you have never used somewhere else. Take note of your password and store it somewhere safe or you will be permanently locked out of your wallet and lose access to your funds. Next, back up your wallet file by selecting File > Backup Wallet. Save the file to a secure location physically separate to your computer, since this will be the only way you can access our funds if anything happens to your computer. For more details on these steps, see here.
Now send exactly 1000 DASH in a single transaction to the new address you generated in the previous step. This may be sent from another wallet, or from funds already held in your current wallet. Once the transaction is complete, view the transaction in a blockchain explorer by searching for the address. You will need 15 confirmations before you can start the masternode, but you can continue with the next step at this point already: installing Dash Core on your VPS.
Install Dash Core¶
Dash Core is the software behind both the Dash Core GUI wallet and Dash masternodes. If not displaying a GUI, it runs as a daemon on your VPS (dashd), controlled by a simple command interface (dash-cli).
Open PuTTY or a console again and connect using the username and password you just created for your new, non-root user. There are two options to install Dash Core, an automated option using a script utility called dashman by Dash Core Team member moocowmoo, and a more complicated option which will allow you to understand all of the key steps involved in preparing your masternode.
Option 1: Automated installation using dashman¶
To install Dash using dashman, enter the following commands after logging in:
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/moocowmoo/dashman
~/dashman/dashman install
(press Y and Enter to confirm)
dashman will download the latest version of Dash Core for your system, as well as an initial snapshot of the blockchain to speed up the bootstrapping process. Next download and install Sentinel, which is required for masternodes at version 0.12.1 or higher:
~/dashman/dashman install sentinel
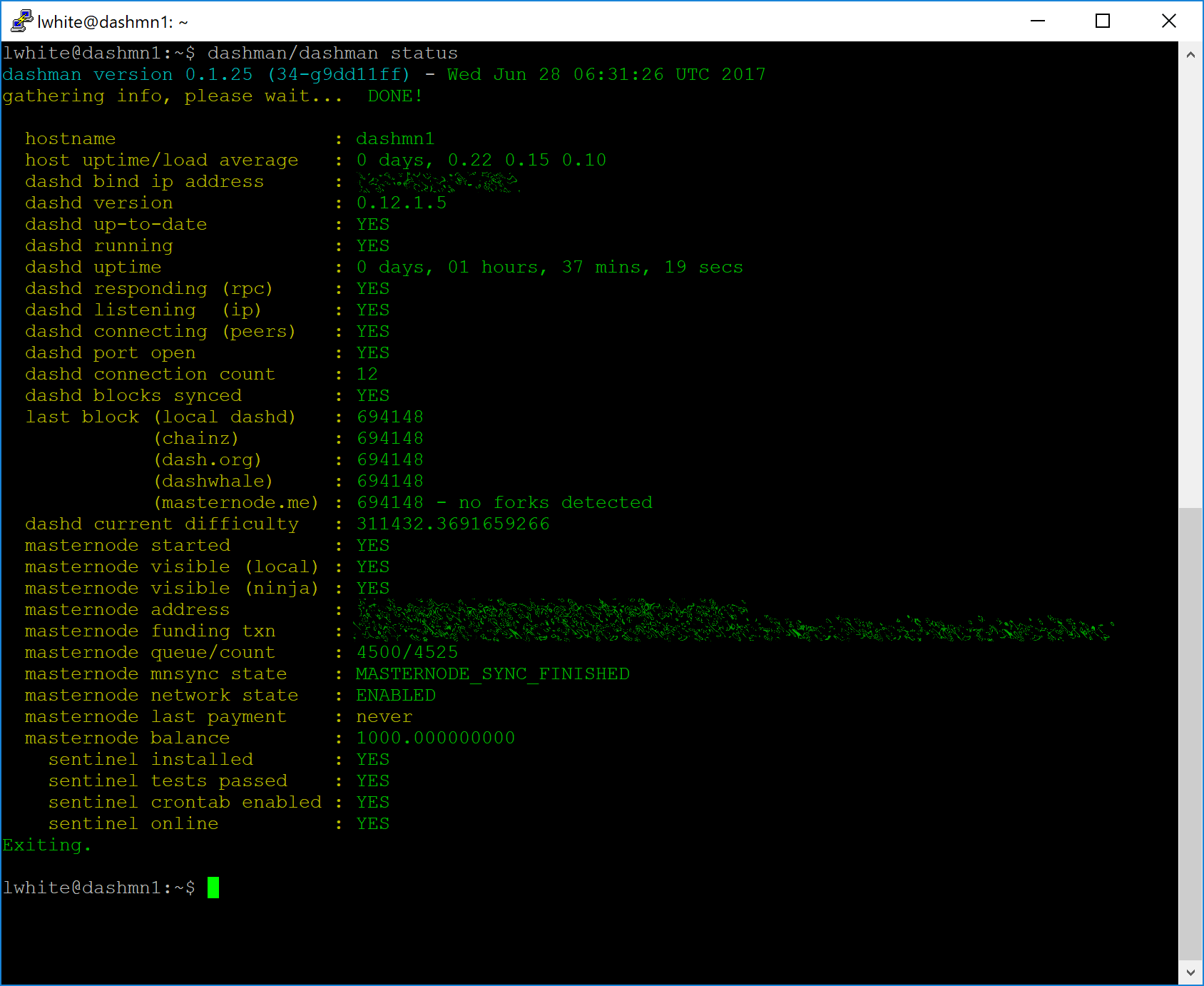
Your system is now running as a standard Dash node, and is busy completing synchronisation with the blockchain. Since dashman does not automatically restart your masternode in the event of a system error, add a check function to crontab to make sure it checks every minute to ensure your masternode is still running:
crontab -e
Choose nano as your editor and enter the following line at the end of the file, after the line for sentinel:
* * * * * pidof dashd || ~/.dashcore/dashd
Press enter to make sure there is a blank line at the end of the file, then press Ctrl + X to close the editor and Y and Enter save the file. Check the sync status and wait until all blockchain synchronisation and the 15 confirmations for the collateral transaction are complete:
~/dashman/dashman status
Continue with the next step to register your masternode.
Option 2: Manual installation¶
To manually download and install the components of your Dash masternode,
visit the GitHub releases page
and copy the link to the latest x86_64-linux-gnu version. Go back to
your terminal window and enter the following command, pasting in the
address to the latest version of Dash Core by right clicking or pressing
Ctrl + V:
cd /tmp
wget https://github.com/dashpay/dash/releases/download/v0.13.3.0/dashcore-0.13.3.0-x86_64-linux-gnu.tar.gz
Verify the integrity of your download by running the following command
and comparing the output against the value for the file as shown in the
SHA256SUMS.asc file:
wget https://github.com/dashpay/dash/releases/download/v0.13.3.0/SHA256SUMS.asc
sha256sum dashcore-0.13.3.0-x86_64-linux-gnu.tar.gz
cat SHA256SUMS.asc
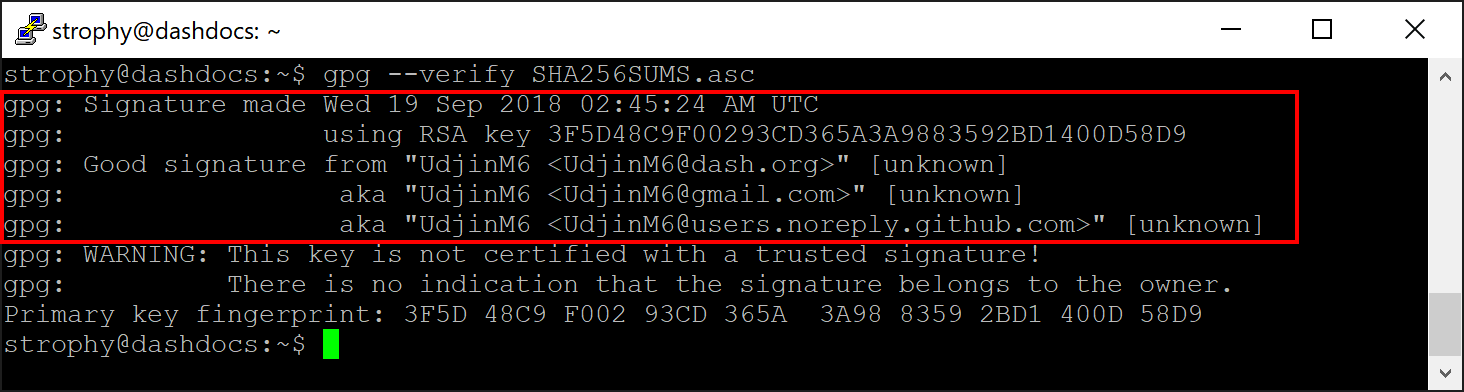
You can also optionally verify the authenticity of your download as an
official release by Dash Core Team. All releases of Dash are signed
using GPG by Alexander Block (codablock) with the key 63A9 6B40 6102 E091, verifiable
here on Keybase. Import the key, download
the ASC file for the current release of Dash and verify the signature as
follows:
curl https://keybase.io/codablock/pgp_keys.asc | gpg --import
gpg --verify SHA256SUMS.asc
Create a working directory for Dash, extract the compressed archive and copy the necessary files to the directory:
mkdir ~/.dashcore
tar xfv dashcore-0.13.3.0-x86_64-linux-gnu.tar.gz
cp -f dashcore-0.13.3/bin/dashd ~/.dashcore/
cp -f dashcore-0.13.3/bin/dash-cli ~/.dashcore/
Create a configuration file using the following command:
nano ~/.dashcore/dash.conf
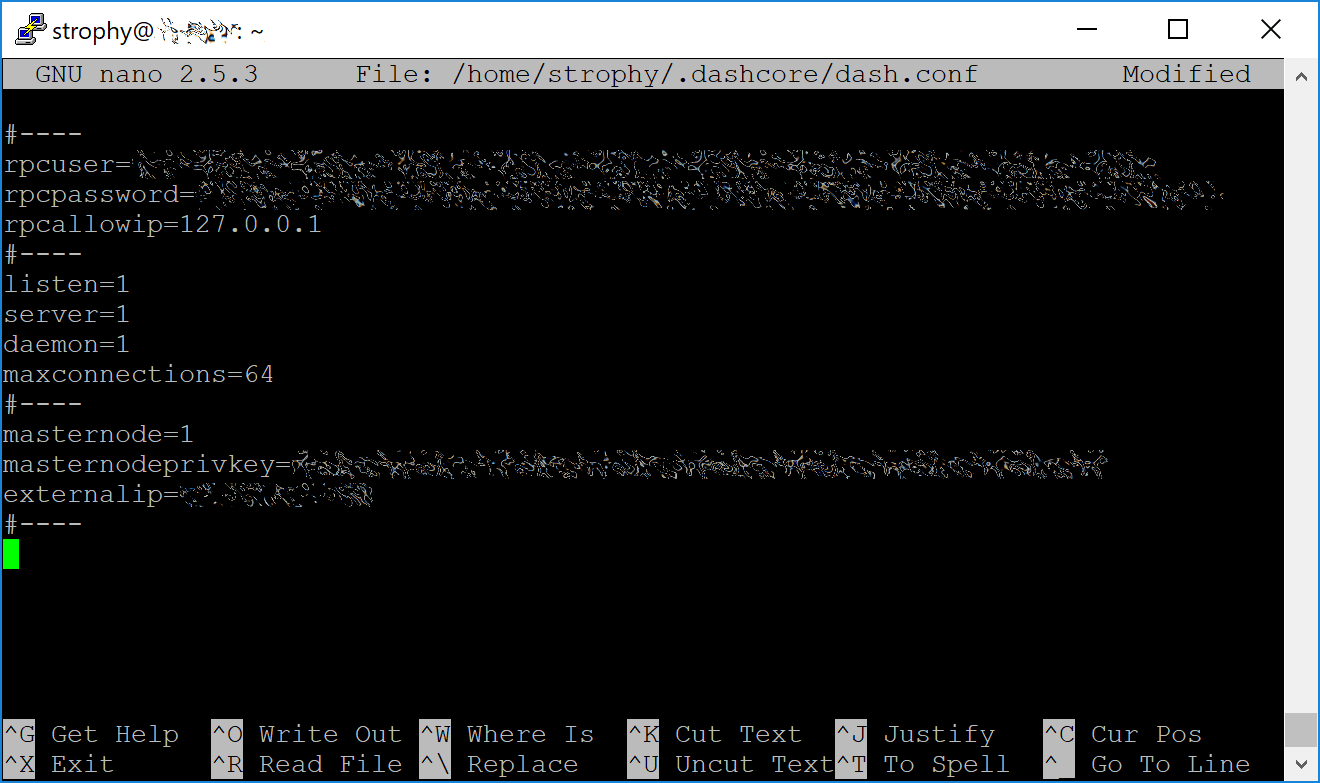
An editor window will appear. We now need to create a configuration file specifying several variables. Copy and paste the following text to get started, then replace the variables specific to your configuration as follows:
#----
rpcuser=XXXXXXXXXXXXX
rpcpassword=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
rpcallowip=127.0.0.1
#----
listen=1
server=1
daemon=1
maxconnections=64
#----
masternode=1
masternodeprivkey=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
externalip=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
#----
Replace the fields marked with XXXXXXX as follows:
rpcuser: enter any string of numbers or letters, no special characters allowedrpcpassword: enter any string of numbers or letters, no special characters allowedmasternodeprivkey: this is the legacy masternode private key you generated in the previous stepexternalip: this is the IP address of your VPS
The result should look something like this:
Press Ctrl + X to close the editor and Y and Enter save the file. You can now start running Dash on the masternode to begin synchronization with the blockchain:
~/.dashcore/dashd
You will see a message reading Dash Core server starting. We will now install Sentinel, a piece of software which operates as a watchdog to communicate to the network that your node is working properly:
cd ~/.dashcore
git clone https://github.com/dashpay/sentinel.git
cd sentinel
virtualenv venv
venv/bin/pip install -r requirements.txt
venv/bin/python bin/sentinel.py
You will see a message reading dashd not synced with network! Awaiting full sync before running Sentinel. Add dashd and sentinel to crontab to make sure it runs every minute to check on your masternode:
crontab -e
Choose nano as your editor and enter the following lines at the end of the file:
* * * * * cd ~/.dashcore/sentinel && ./venv/bin/python bin/sentinel.py 2>&1 >> sentinel-cron.log
* * * * * pidof dashd || ~/.dashcore/dashd
Press enter to make sure there is a blank line at the end of the file, then press Ctrl + X to close the editor and Y and Enter save the file. We now need to wait for 15 confirmations of the collateral transaction to complete, and wait for the blockchain to finish synchronizing on the masternode. You can use the following commands to monitor progress:
~/.dashcore/dash-cli mnsync status
When synchronisation is complete, you should see the following response:
{
"AssetID": 999,
"AssetName": "MASTERNODE_SYNC_FINISHED",
"Attempt": 0,
"IsBlockchainSynced": true,
"IsMasternodeListSynced": true,
"IsWinnersListSynced": true,
"IsSynced": true,
"IsFailed": false
}
Continue with the next step to construct the ProTx transaction required to enable your masternode.
Register your masternode¶
DIP003 introduces several changes to how a masternode is set up and operated. These are described briefly under DIP003 Masternode Changes in this documentation, or in full detail in DIP003 itself. It is highly recommended to first read at least the brief documentation before continuing in order to familiarize yourself with the new concepts in DIP003.
Option 1: Registering from a hardware wallet¶
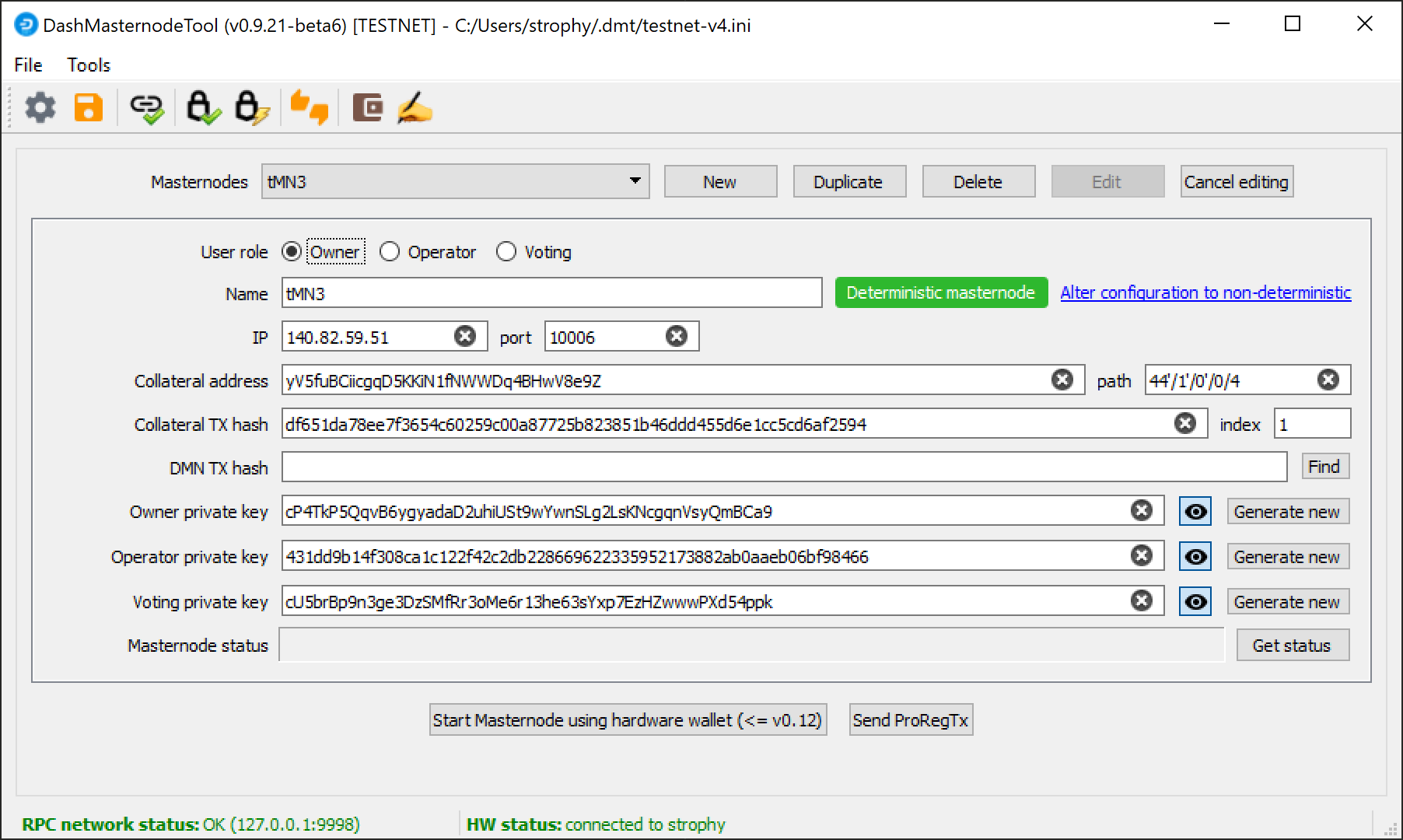
Go back to DMT and ensure that all fields from the previous step are still filled out correctly. Click Generate new for the three private keys required for a DIP003 deterministic masternode:
- Owner private key
- Operator private key
- Voting private key
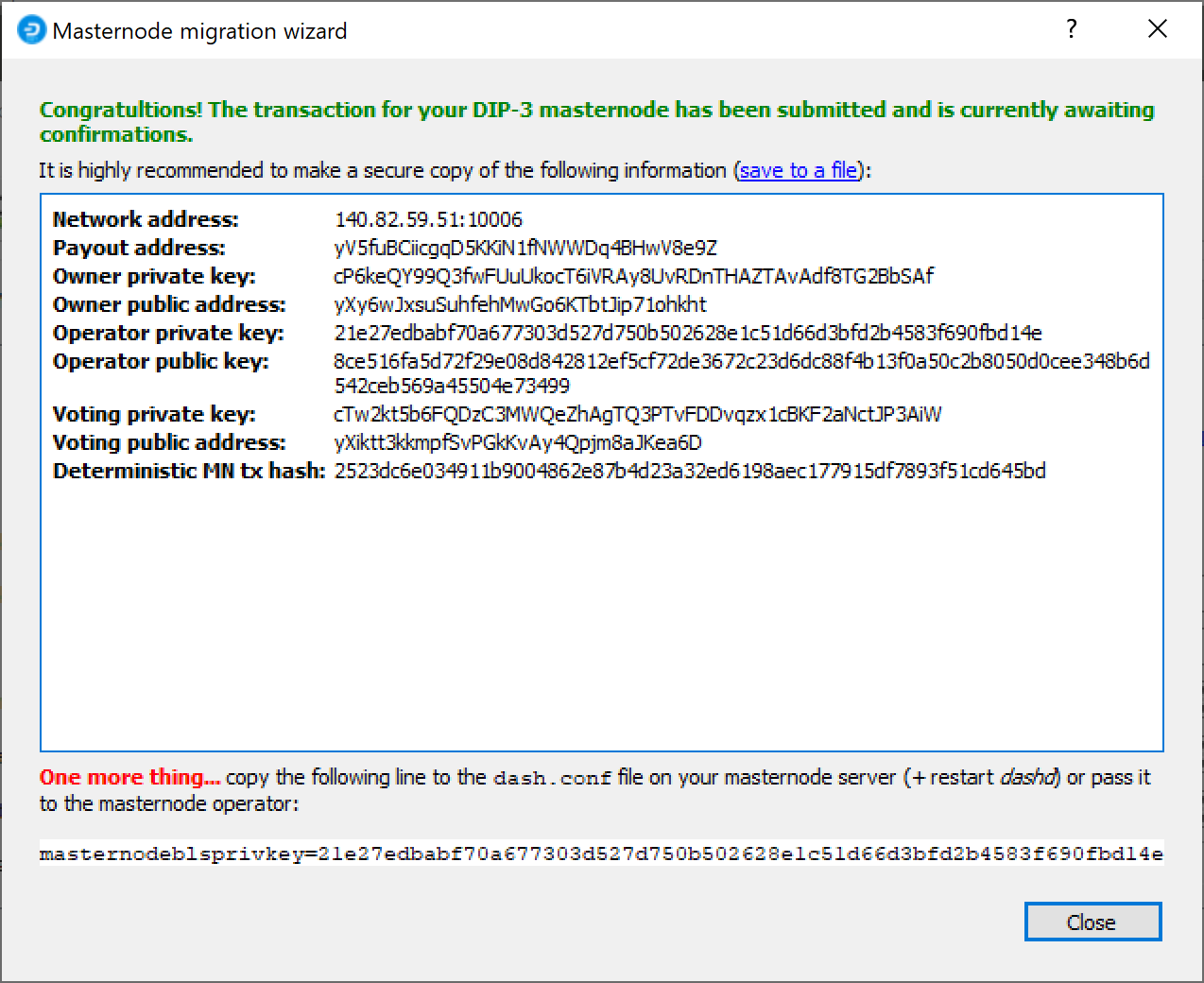
Then click Send ProRegTx and confirm the following two messages:
The BLS secret key must be entered in the dash.conf file on the
masternode. This allows the masternode to watch the blockchain for
relevant Pro*Tx transactions, and will cause it to start serving as a
masternode when the signed ProRegTx is broadcast by the owner, as we
just did above. Edit the configuration file on your masternode as
follows:
nano ~/.dashcore/dash.conf
The editor appears with the existing masternode configuration. Add this line to the end of the file, replacing the key with your BLS secret key generated above:
masternodeblsprivkey=21e27edbabf70a677303d527d750b502628e1c51d66d3bfd2b4583f690fbd14e
Press enter to make sure there is a blank line at the end of the file, then press Ctrl + X to close the editor and Y and Enter save the file. We now need to restart the masternode for this change to take effect. Enter the following commands, waiting a few seconds in between to give Dash Core time to shut down:
~/.dashcore/dash-cli stop
sleep 5
~/.dashcore/dashd
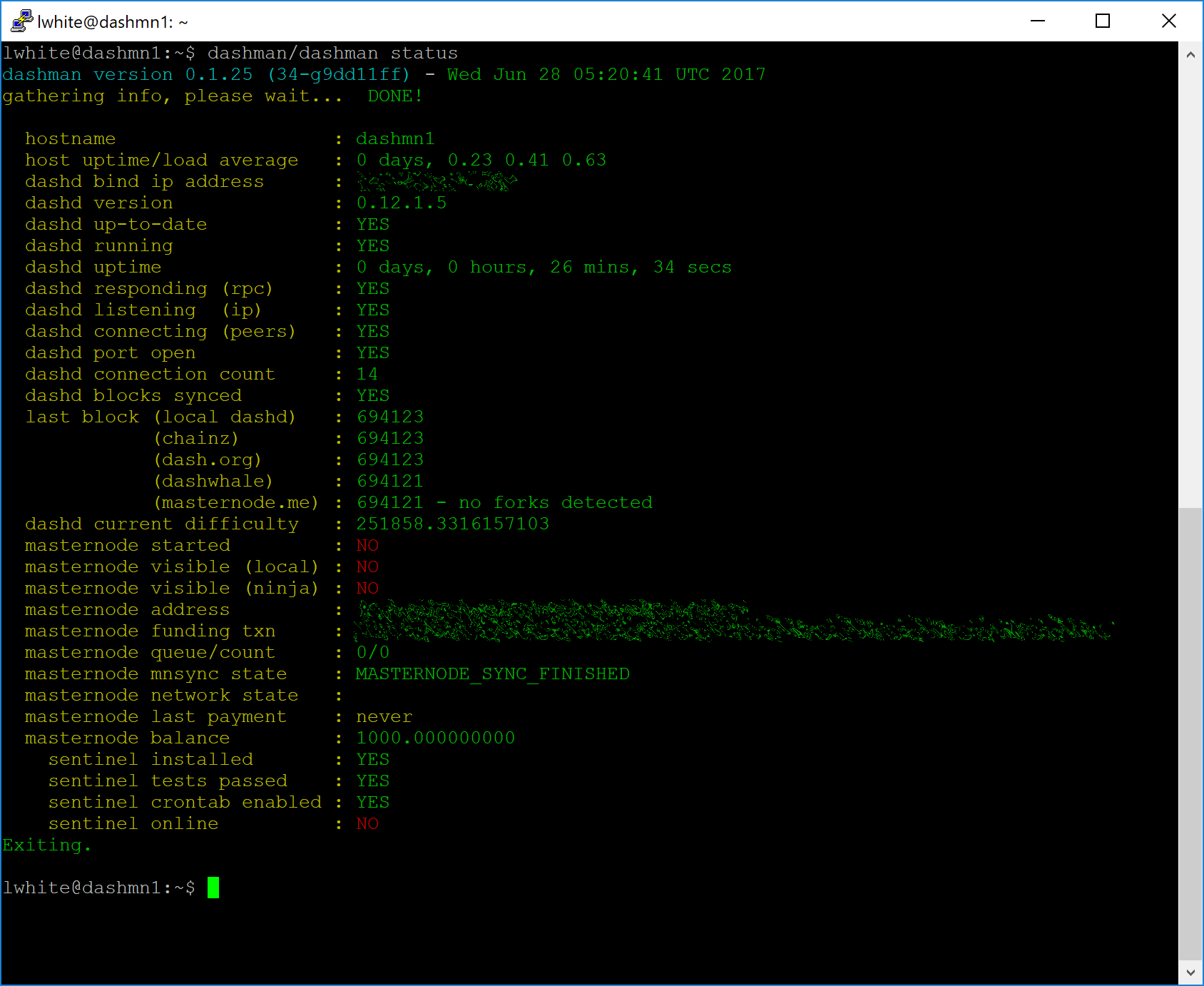
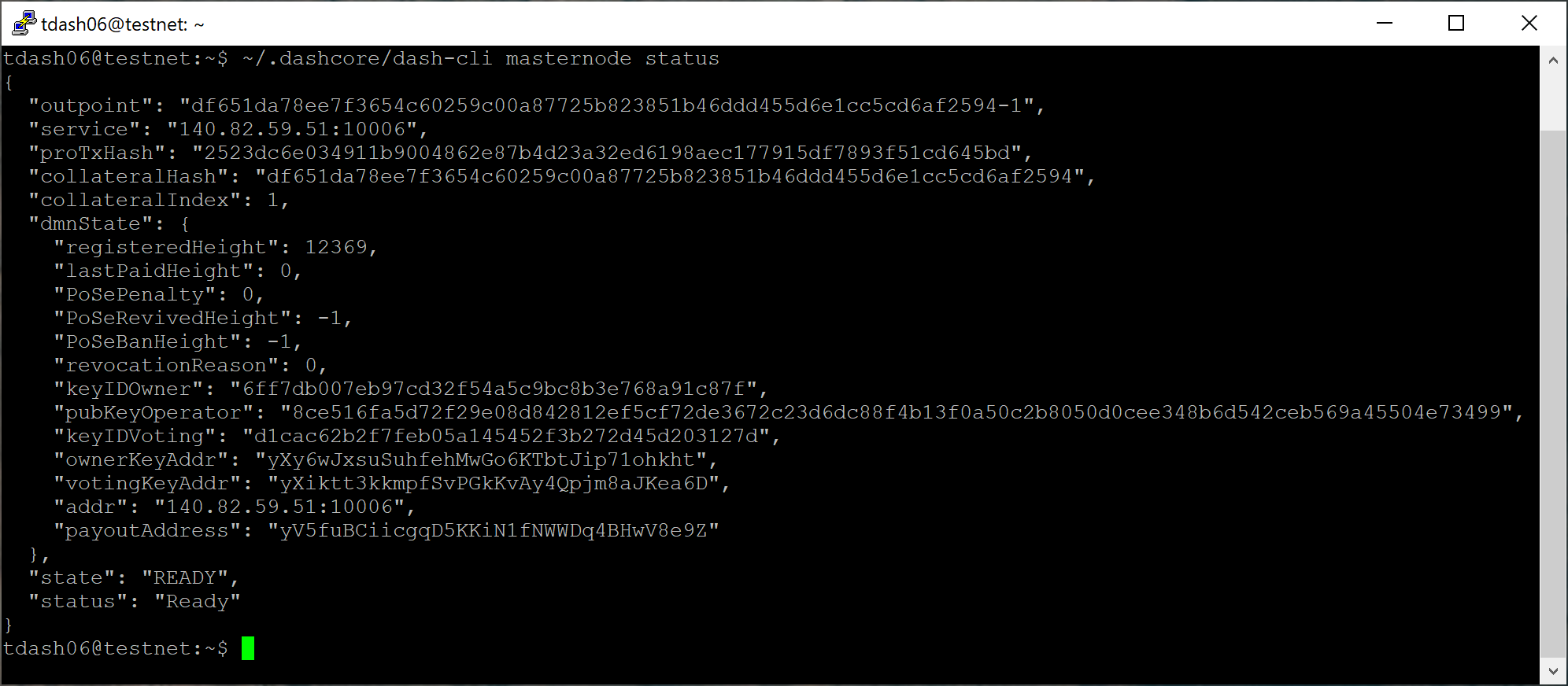
At this point you can monitor your masternode using
dashman/dashman status, by entering
~/.dashcore/dash-cli masternode status or using the Get status
function in DMT. The final result should appear as follows:
At this point you can safely log out of your server by typing exit.
Congratulations! Your masternode is now running.
Option 2: Registering from Dash Core wallet¶
Identify the funding transaction¶
If you used an address in Dash Core wallet for your collateral transaction, you now need to find the txid of the transaction. Click Tools > Debug console and enter the following command:
masternode outputs
This should return a string of characters similar to this:
{
"ad308ec104bdf113444be609eb3dce9474a5550424204c6538843e3ccd3d4e78" : "1",
}
The first long string is your transaction hash, while the last number is the index.
Generate a BLS key pair¶
A public/private BLS key pair is required for the operator of the masternode. If you are using a hosting service, they may provide you with their public key, and you can skip this step. If you are hosting your own masternode or have agreed to provide your host with the BLS private key, generate a BLS public/private keypair as follows:
bls generate
{
"secret": "28a85abb5aa8e820f65e33974cef0ab0bf06195f61454d2feb7fa578612d2228",
"public": "144cbf4d472716b9504a54c7ca26906a3346253b787ffeb1a4999325049f5b2c51ef2e7c215d85f0a9142ec1c78db99b"
}
These keys are NOT stored by the wallet and must be kept secure,
similar to the value provided in the past by the masternode genkey
command.
Add the private key to your masternode configuration¶
The public key will be used in following steps. The private key must be
entered in the dash.conf file on the masternode. This allows the
masternode to watch the network for relevant Pro*Tx transactions, and
will cause it to start serving as a masternode when the signed ProRegTx
is broadcast by the owner (final step below). Log in to your masternode
using ssh or PuTTY and edit the configuration file on your
masternode as follows:
nano ~/.dashcore/dash.conf
The editor appears with the existing masternode configuration. Add this line to the end of the file, replacing the key with your BLS secret key generated above:
masternodeblsprivkey=28a85abb5aa8e820f65e33974cef0ab0bf06195f61454d2feb7fa578612d2228
Press enter to make sure there is a blank line at the end of the file, then press Ctrl + X to close the editor and Y and Enter save the file. We now need to restart the masternode for this change to take effect. Enter the following commands, waiting a few seconds in between to give Dash Core time to shut down:
~/.dashcore/dash-cli stop
sleep 5
~/.dashcore/dashd
We will now prepare the transaction used to register a DIP003 masternode on the network.
Prepare a ProRegTx transaction¶
First, we need to get a new, unused address from the wallet to serve as the owner address. This is different to the collateral address. It must also be used as the voting address if Spork 15 is not yet active. Generate a new address as follows:
getnewaddress
yMwR1zf2Cv9gcMdHULRVbTTMGw7arvpbM5
Then either generate or choose an existing second address to receive the owner’s masternode payouts. It is also possible to use an address external to the wallet:
getnewaddress
yLqyR8PHEB7Fp1ue8nSuLfuxQhrj5PSTDv
You can also optionally generate and fund a third address to pay the transaction fee. If you selected an external payout address, you must specify a fee source address. Either the payout address or fee source address must have enough balance to pay the transaction fee, or the final register_submit transaction will fail.
The private keys to the owner and fee source addresses must exist in the wallet submitting the transaction to the network. If your wallet is protected by a password, it must now be unlocked to perform the following commands. Unlock your wallet for 5 minutes:
walletpassphrase yourSecretPassword 300
We will now prepare an unsigned ProRegTx special transaction using the
protx register_prepare command. This command has the following
syntax:
protx register_prepare collateralHash collateralIndex ipAndPort ownerKeyAddr
operatorPubKey votingKeyAddr operatorReward payoutAddress (feeSourceAddress)
Open a text editor such as notepad to prepare this command. Replace each argument to the command as follows:
collateralHash: The txid of the 1000 Dash collateral funding transactioncollateralIndex: The output index of the 1000 Dash funding transactionipAndPort: Masternode IP address and port, in the formatx.x.x.x:yyyyownerKeyAddr: The new Dash address generated above for the owner/voting addressoperatorPubKey: The BLS public key generated above (or provided by your hosting service)votingKeyAddr: The new Dash address generated above, or the address of a delegate, used for proposal votingoperatorReward: The percentage of the block reward allocated to the operator as paymentpayoutAddress: A new or existing Dash address to receive the owner’s masternode rewardsfeeSourceAddress: An (optional) address used to fund ProTx fee.payoutAddresswill be used if not specified.
Note that the operator is responsible for specifying their own
reward address in a separate update_service
transaction if you specify a non-zero operatorReward. The owner of
the masternode collateral does not specify the operator’s payout
address.
Example (remove line breaks if copying):
protx register_prepare
ad308ec104bdf113444be609eb3dce9474a5550424204c6538843e3ccd3d4e78
1
140.82.59.51:9999
yMwR1zf2Cv9gcMdHULRVbTTMGw7arvpbM5
144cbf4d472716b9504a54c7ca26906a3346253b787ffeb1a4999325049f5b2c51ef2e7c215d85f0a9142ec1c78db99b
yMwR1zf2Cv9gcMdHULRVbTTMGw7arvpbM5
0
yLqyR8PHEB7Fp1ue8nSuLfuxQhrj5PSTDv
Output:
{
"tx": "0300010001784e3dcd3c3e8438654c20240455a57494ce3deb09e64b4413f1bd04c18e30ad0000000000feffffff01cccfa204000000001976a9141ea44ced396667eb7d1c5b3699e04b5b3046ecfb88ac00000000d1010000000000784e3dcd3c3e8438654c20240455a57494ce3deb09e64b4413f1bd04c18e30ad0100000000000000000000000000ffff8c523b33271411c59262c9633a1bb810a7fc2b833c43cfa852ab144cbf4d472716b9504a54c7ca26906a3346253b787ffeb1a4999325049f5b2c51ef2e7c215d85f0a9142ec1c78db99b11c59262c9633a1bb810a7fc2b833c43cfa852ab00001976a91405c5fed6a3eb0b92ea5119039efae7a8dee5456488ac4e6cc5451440a6044dbd04d33a11f4cddc9021532ede3012ebbc31c0bb4ceb9c00",
"collateralAddress": "yiFfzbwiN9oneftd7cEfr3kQLRwQ4kp7ue",
"signMessage": "yLqyR8PHEB7Fp1ue8nSuLfuxQhrj5PSTDv|0|yMwR1zf2Cv9gcMdHULRVbTTMGw7arvpbM5|yMwR1zf2Cv9gcMdHULRVbTTMGw7arvpbM5|4e00de34ee03d28adb4e1fdaec966ae239c11da7e6115f566fc4b3f75c8a5503"
}
Next we will use the collateralAddress and signMessage fields to
sign the transaction, and the output of the tx field to submit the
transaction.
Sign the ProRegTx transaction¶
We will now sign the content of the signMessage field using the
private key for the collateral address as specified in
collateralAddress. Note that no internet connection is required for
this step, meaning that the wallet can remain disconnected from the
internet in cold storage to sign the message. In this example we will
again use Dash Core, but it is equally possible to use the signing
function of a hardware wallet. The command takes the following syntax:
signmessage collateralAddress signMessage
Example:
signmessage yiFfzbwiN9oneftd7cEfr3kQLRwQ4kp7ue yLqyR8PHEB7Fp1ue8nSuLfuxQhrj5PSTDv|0|yMwR1zf2Cv9gcMdHULRVbTTMGw7arvpbM5|yMwR1zf2Cv9gcMdHULRVbTTMGw7arvpbM5|4e00de34ee03d28adb4e1fdaec966ae239c11da7e6115f566fc4b3f75c8a5503
Output:
H3ub9BATtvuV+zDGdkUQNoUGpaYFr/O1FypmrSmH5WJ0KFRi8T10FSew0EJO/+Ij+OLv4r0rt+HS9pQFsZgc2dE=
Submit the signed message¶
We will now submit the ProRegTx special transaction to the blockchain to register the masternode. This command must be sent from a Dash Core wallet holding a balance, since a standard transaction fee is involved. The command takes the following syntax:
protx register_submit tx sig
Where:
tx: The serialized transaction previously returned in thetxoutput field from theprotx register_preparecommandsig: The message signed with the collateral key from thesignmessagecommand
Example:
protx register_submit 0300010001784e3dcd3c3e8438654c20240455a57494ce3deb09e64b4413f1bd04c18e30ad0000000000feffffff01cccfa204000000001976a9141ea44ced396667eb7d1c5b3699e04b5b3046ecfb88ac00000000d1010000000000784e3dcd3c3e8438654c20240455a57494ce3deb09e64b4413f1bd04c18e30ad0100000000000000000000000000ffff8c523b33271411c59262c9633a1bb810a7fc2b833c43cfa852ab144cbf4d472716b9504a54c7ca26906a3346253b787ffeb1a4999325049f5b2c51ef2e7c215d85f0a9142ec1c78db99b11c59262c9633a1bb810a7fc2b833c43cfa852ab00001976a91405c5fed6a3eb0b92ea5119039efae7a8dee5456488ac4e6cc5451440a6044dbd04d33a11f4cddc9021532ede3012ebbc31c0bb4ceb9c00 H3ub9BATtvuV+zDGdkUQNoUGpaYFr/O1FypmrSmH5WJ0KFRi8T10FSew0EJO/+Ij+OLv4r0rt+HS9pQFsZgc2dE=
Output:
b823338301e47875493c20361a23aef034578030c639480203b394669ab05e09
Your masternode is now registered and will appear on the Deterministic
Masternode List after the transaction is mined to a block. You can view
this list on the Masternodes -> DIP3 Masternodes tab of the Dash
Core wallet, or in the console using the command protx list valid,
where the txid of the final protx register_submit transaction
identifies your DIP003 masternode. Note again that all functions related
to DIP003 will only take effect once Spork 15 is enabled on the network.
You can view the spork status using the spork active command.
At this point you can go back to your terminal window and monitor your
masternode using dashman/dashman status, by entering
~/.dashcore/dash-cli masternode status or using the Get status
function in DMT. The final result should appear as follows:
At this point you can safely log out of your server by typing exit.
Congratulations! Your masternode is now running.