Dashmate#
Dashmate is a universal tool designed to help you set up and run Dash masternodes in a containerized environment. It is also an ideal tool to quickly and easily set up and run a development network on your local system.
Setting up a testnet evonode using dashmate#
Instalação#
Install dependencies#
Install and configure Docker:
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh && sh ./get-docker.sh
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp docker
Install dashmate#
There are several methods available for installing dashmate.
Debian package#
Download the dashmate installation package:
wget https://github.com/dashpay/platform/releases/download/v0.25.15/dashmate_0.25.15-1_arm64.deb
Install dashmate using apt:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ./dashmate_0.25.15-1_arm64.deb
Node package#
To install the NodeJS package, it is necessary to install NodeJS first. We recommend installing it using nvm:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.5/install.sh | bash
source ~/.bashrc
nvm install 20
Once NodeJS has been installed, use npm to install dashmate:
npm install -g dashmate
Masternode setup#
You can setup both regular masternodes and Evolution masternodes (evonodes) using dashmate. There are few minor extra steps for evonodes, but the process is largely identical for both masternode types. Complete the steps in the sections below to set up your node or follow along with this step-by-step tutorial.
To begin masternode setup, run dashmate setup to start the interactive wizard:
dashmate setup
Set Network and Node type#
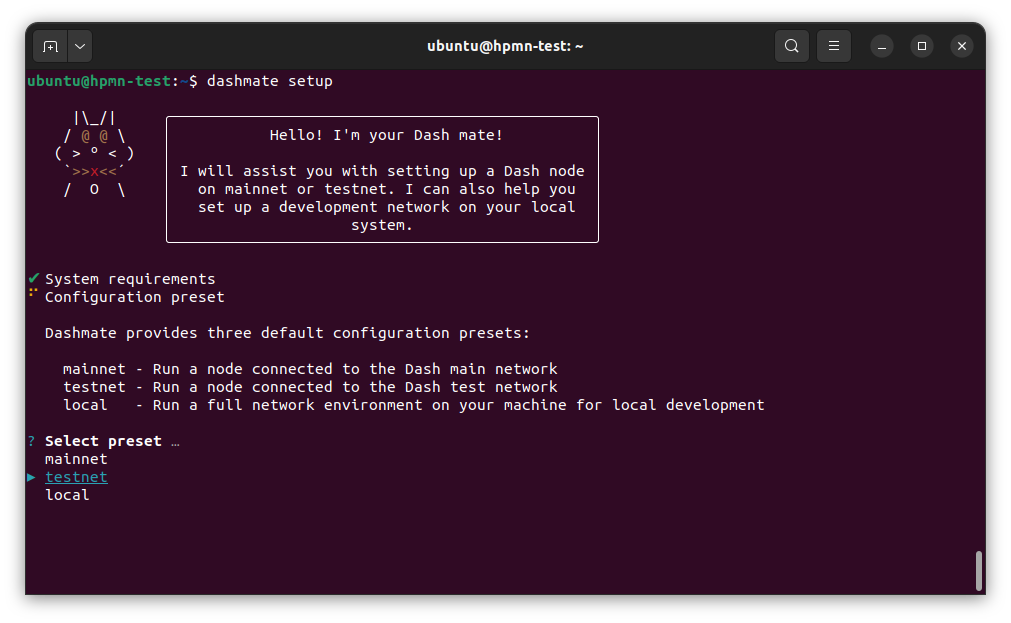
Select the testnet network preset#
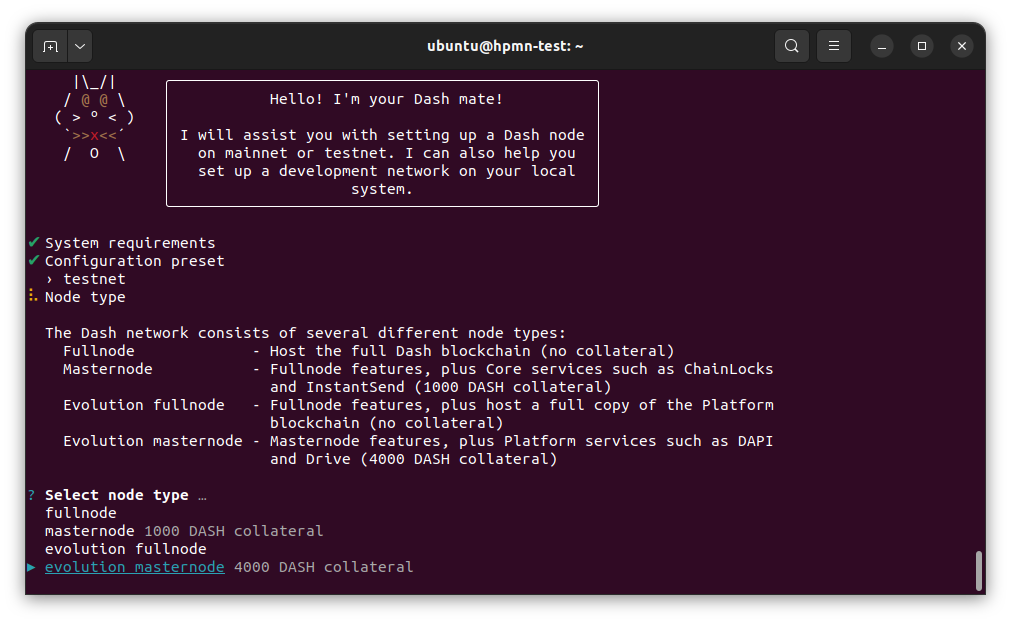
Create an Evolution masternode#
Select No to register a new masternode or Yes to import information about an existing masternode.
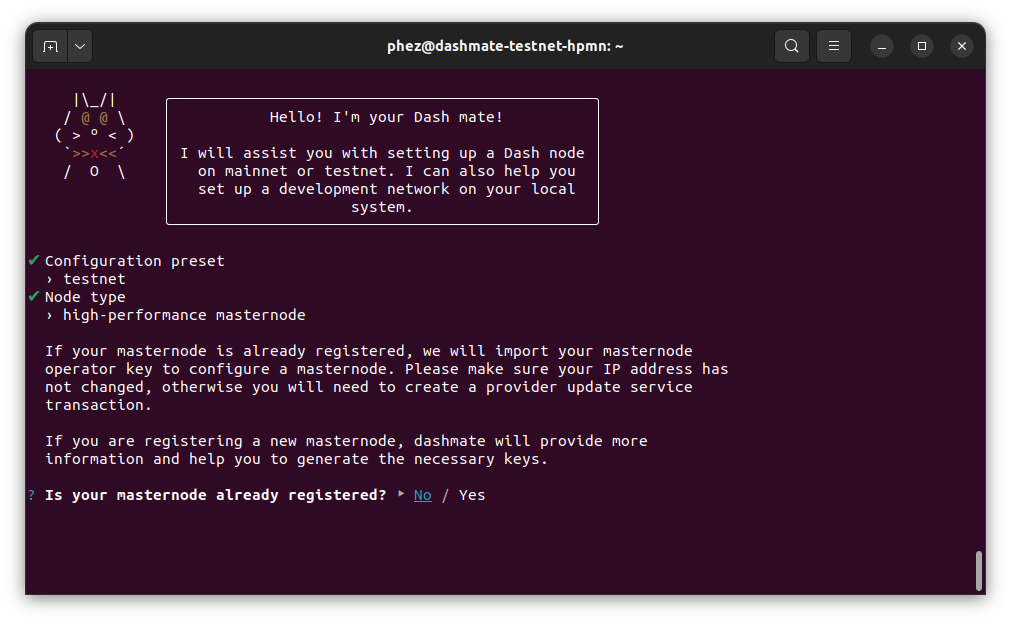
Set up a new masternode#
Define Keys and Addresses#
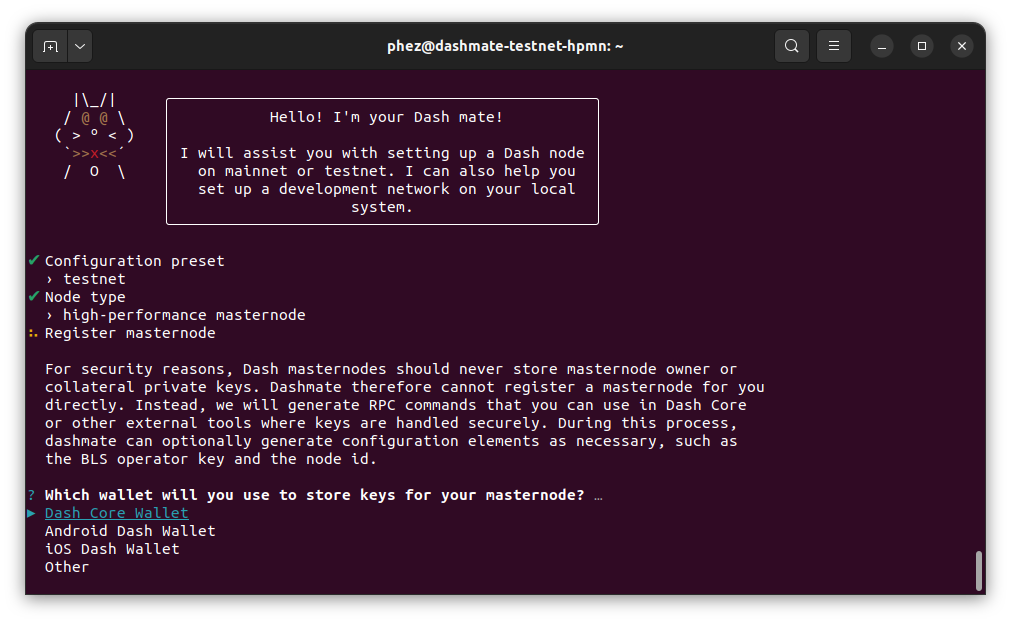
Store masternode keys in Dash Core#
Enter the requested information from your collateral funding transaction. You can find these values using Dash Core’s masternode outputs command.
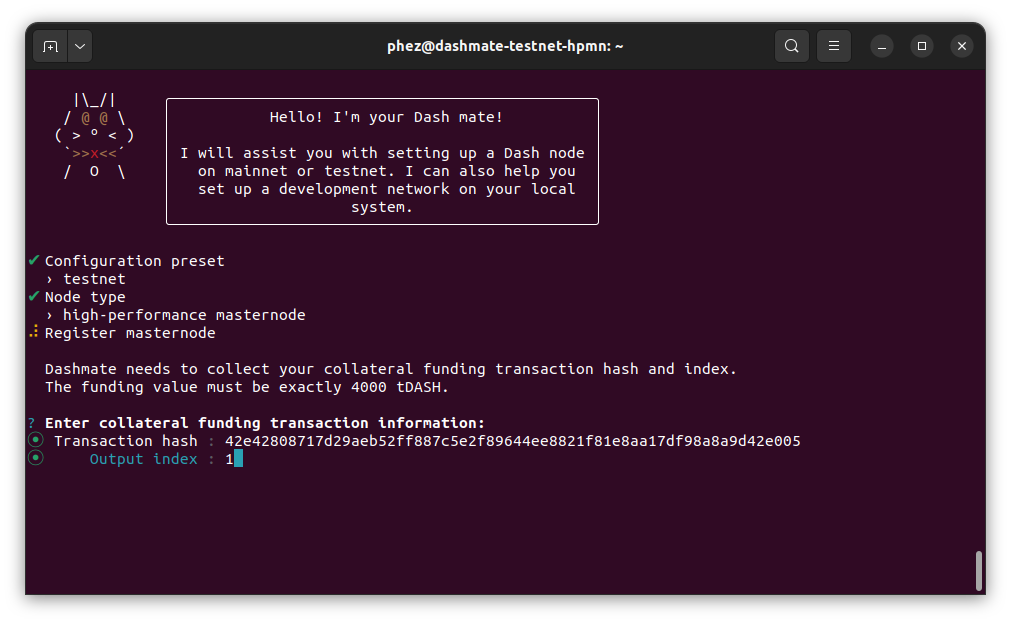
Enter collateral transaction information#
Enter the owner, voting, and payout addresses you generated using Dash Core or your selected wallet.
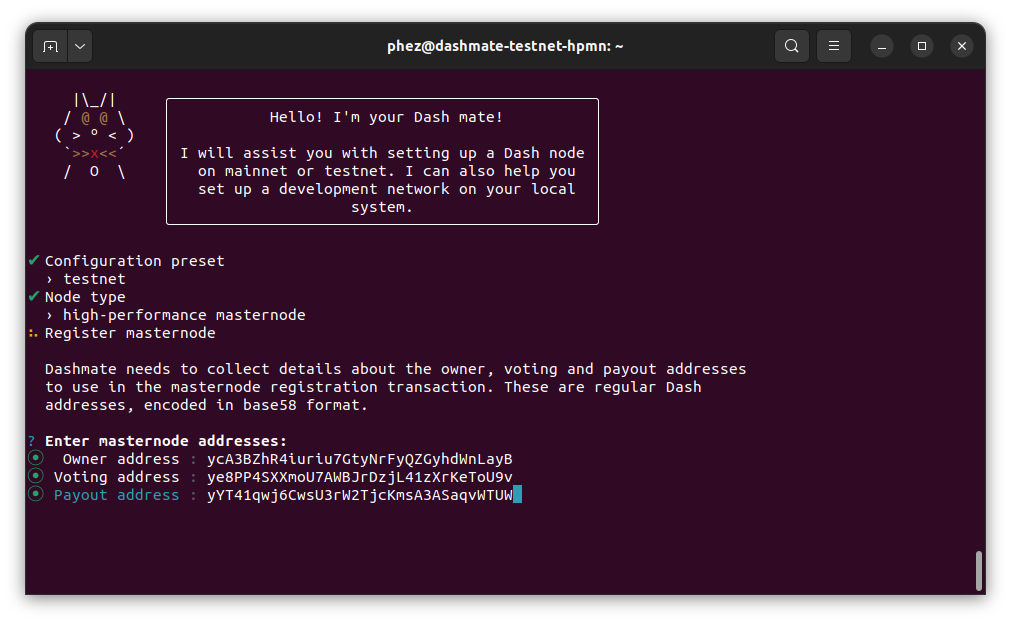
Enter masternode addresses#
Enter an operator BLS private key. You can enter one you have created (e.g. using Dash Core) or received from a hosting provider. Optionally, use the one automatically generated by dashmate.
If a portion of the masternode rewards are intended to go to the operator directly, set the reward share percentage also.
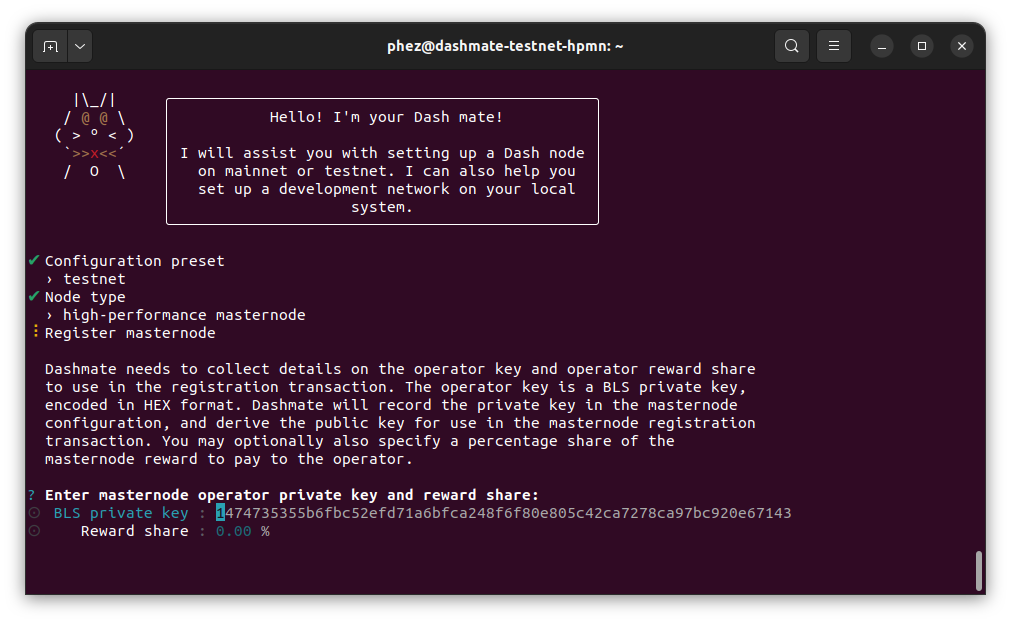
Enter operator information#
Nota
The following step only applies to Evolution masternodes. Regular masternodes do not require a Platform node key since they do not host Platform services.
Enter a Platform node key. You can enter one you have created or received from a hosting provider. Optionally, use the one automatically generated by dashmate.
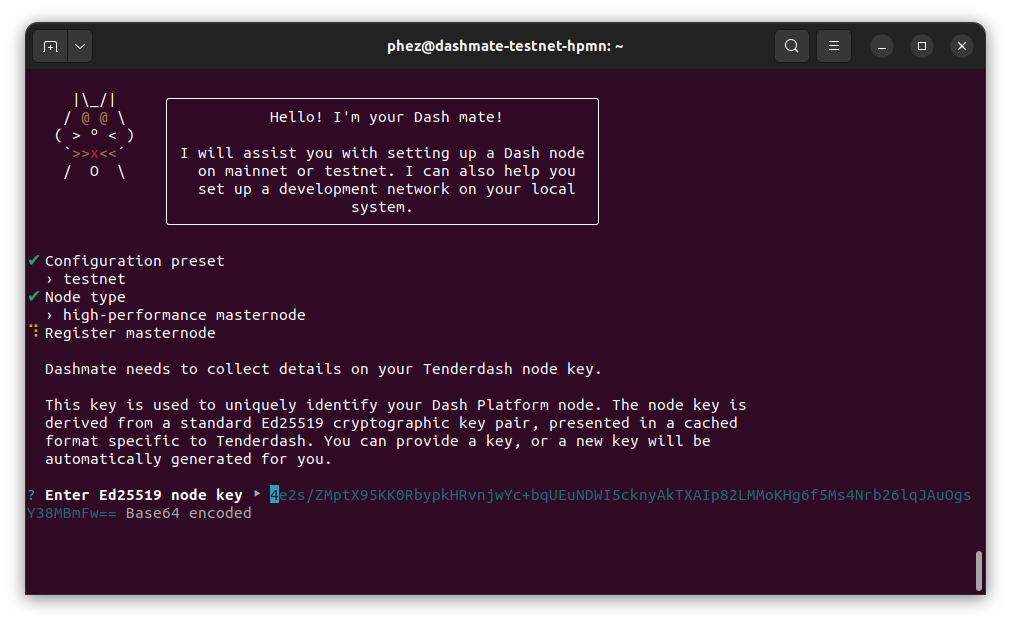
Enter the Platform node key#
Configure communication#
Dashmate will automatically detect the external IP address and select the default ports for the network you are setting up. You can modify these values if necessary for a specific reason, but typically the defaults should be used.
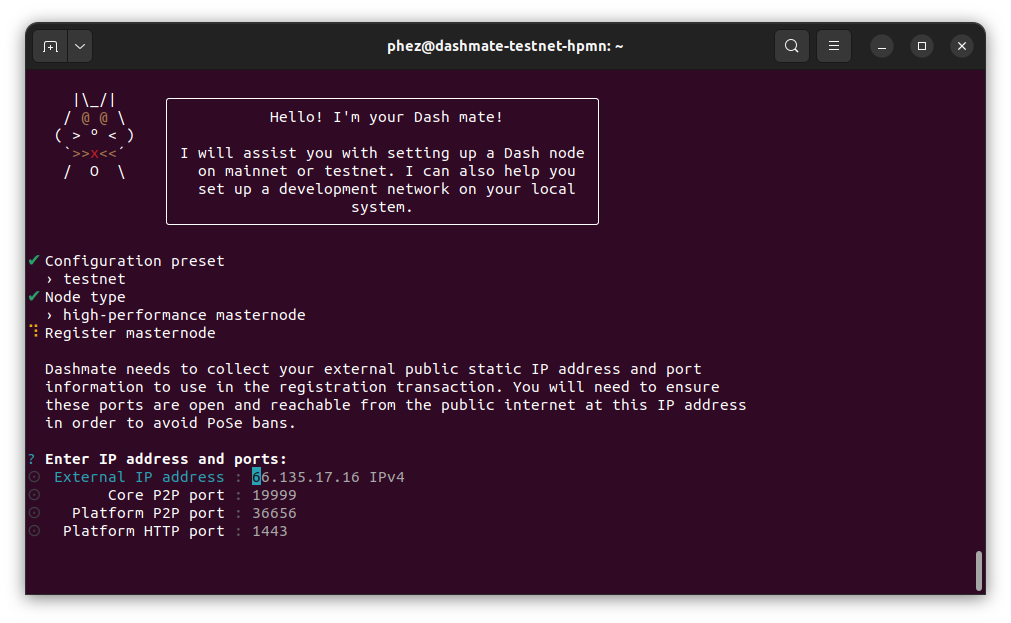
Enter connection information#
Register the masternode#
Copy the provided protx command and run it using dash-cli or the Dash Core console. Do note that your payout address must have a balance for the registration process to be successful, so remember to send some DASH to this address before you begin registration.
Select Yes after the command has been run successfully. If you receive an error, select No to go back through the previous steps and review details.
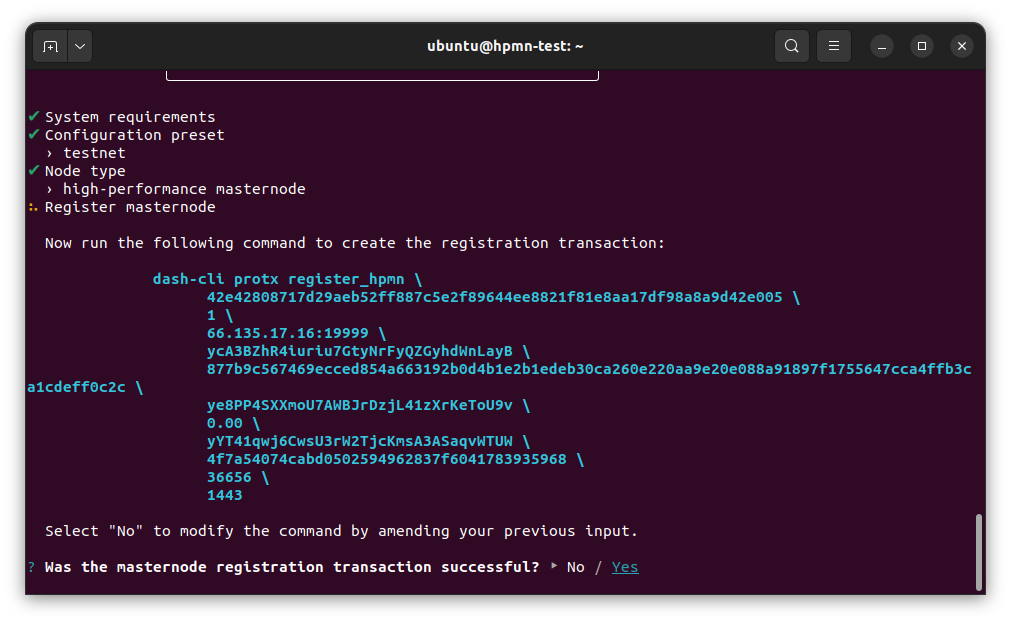
Run the registration command#
Enable SSL#
Nota
The following step only applies to evonodes. Regular masternodes do not require an SSL certificate since they do not host Platform services.
Dash Platform requires SSL for communication. Dashmate provides several options for obtaining the required SSL certificate.
Aviso
Self-signed certificates cannot be used on mainnet. When setting up a mainnet evonode, ZeroSSL and File on disk are the only options available.
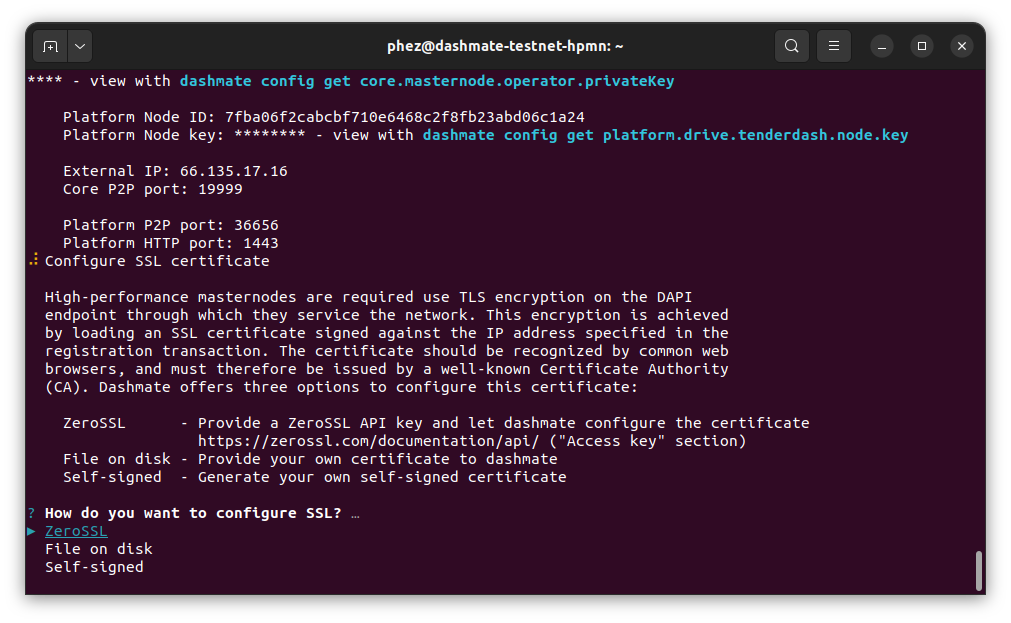
Configure SSL#
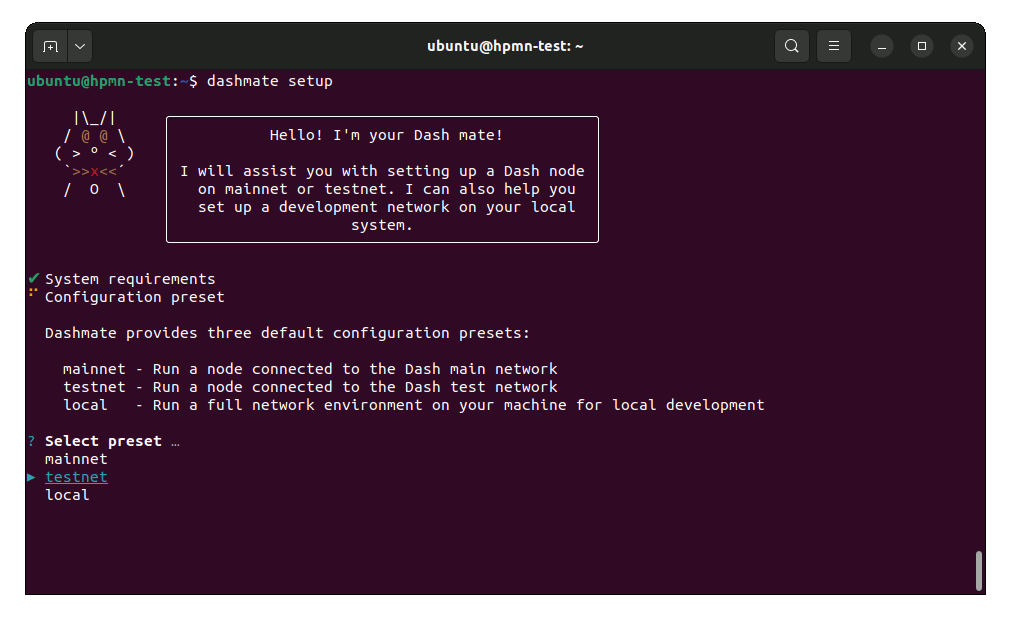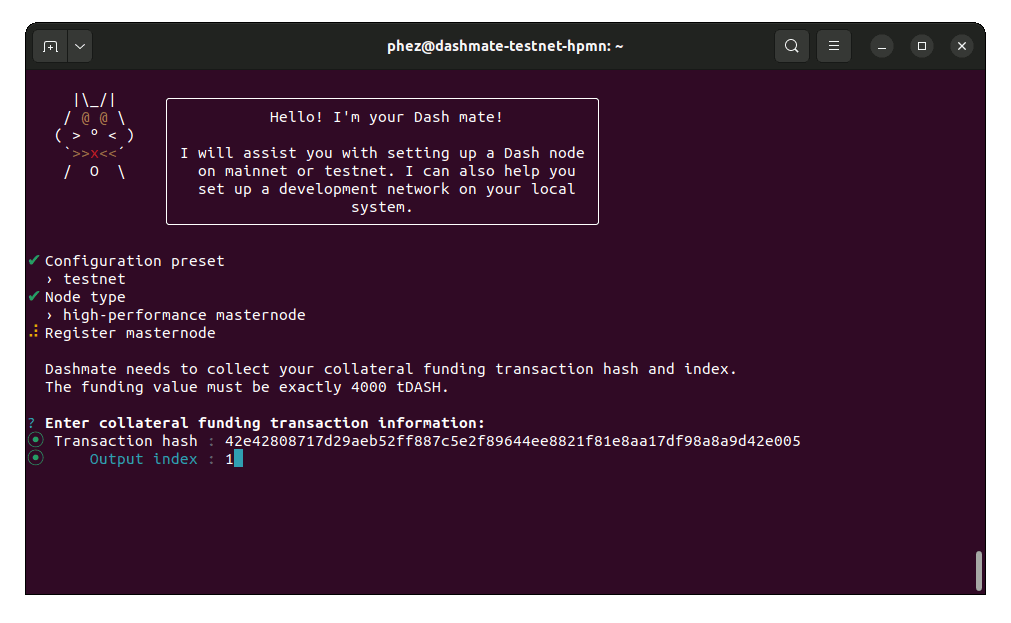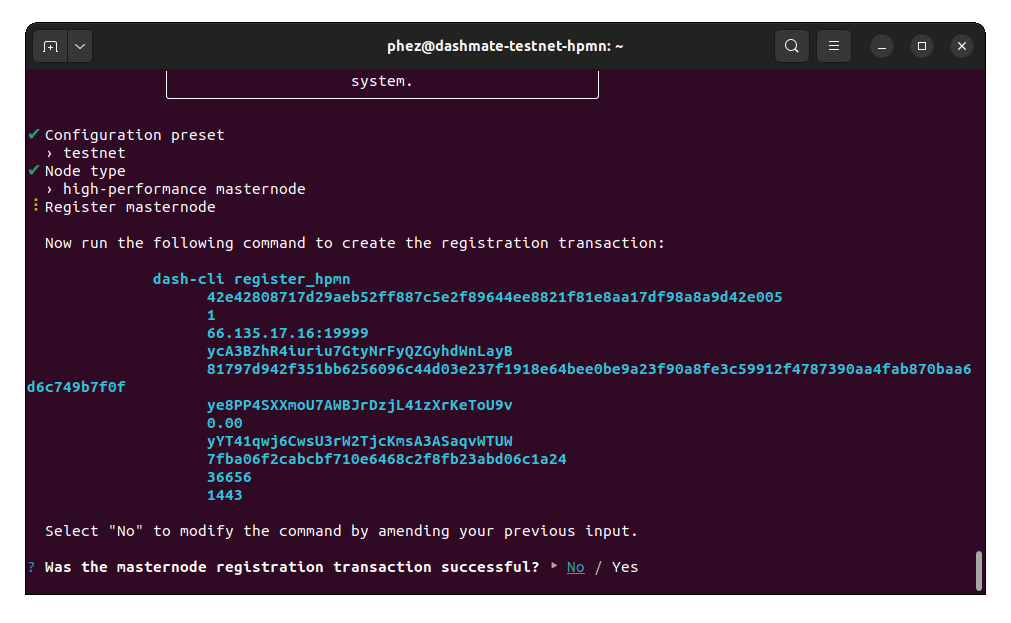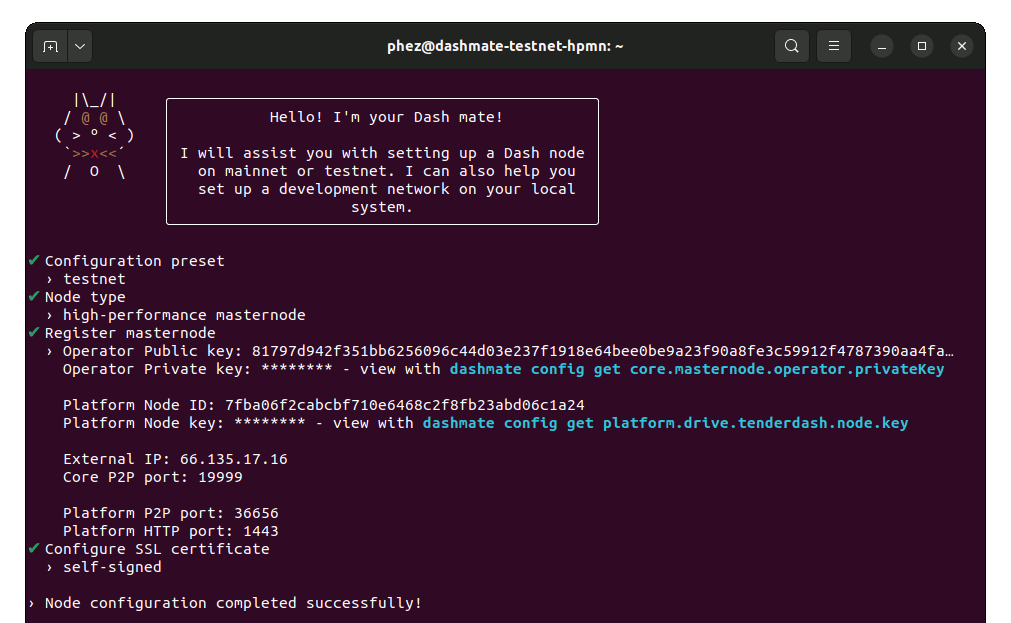
Once the configuration is complete, a summary showing the network and type of node configured is displayed. This summary includes important parameters and information on how to proceed.
Aviso
The BLS operator private key and Platform Node key must be backed up and kept secure.
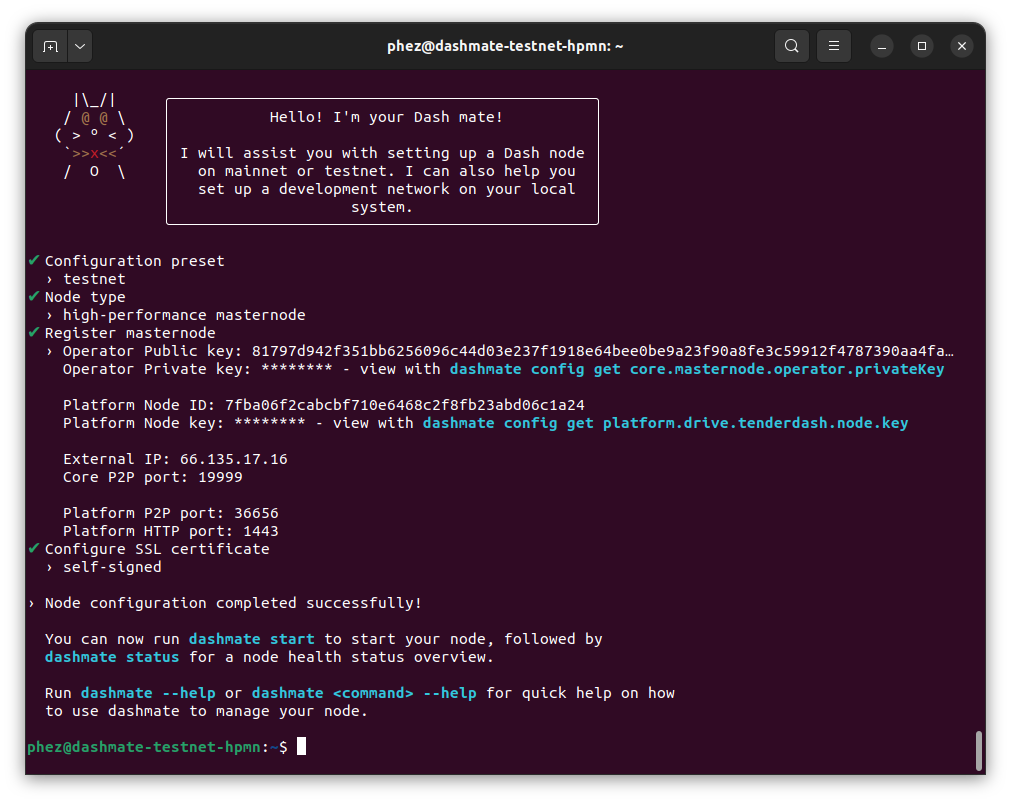
Configuration complete! 🎉#
Start the node#
Start your node as follows:
dashmate start
Nota
When starting a node for the first time, dashmate will download the Docker images required for each service. The time required for this one-time download will depend on the available bandwidth but typically should complete within a few minutes.
Dashmate node operation#
You can manage your masternode status, configuration, and running state entirely from within dashmate. Use the built-in help system to learn more:
dashmate --helpdashmate <command> --help
Dashmate displaying top-level help output#
Start or restart node#
To start your dashmate node, run:
dashmate start
To restart your dashmate node, run:
dashmate restart
Stop node#
To stop your dashmate node, run:
dashmate stop
Node status#
You can check the status of your masternode using the various dashmate
status commands as follows:
dashmate status
dashmate status core
dashmate status host
dashmate status masternode
dashmate status platform
dashmate status services
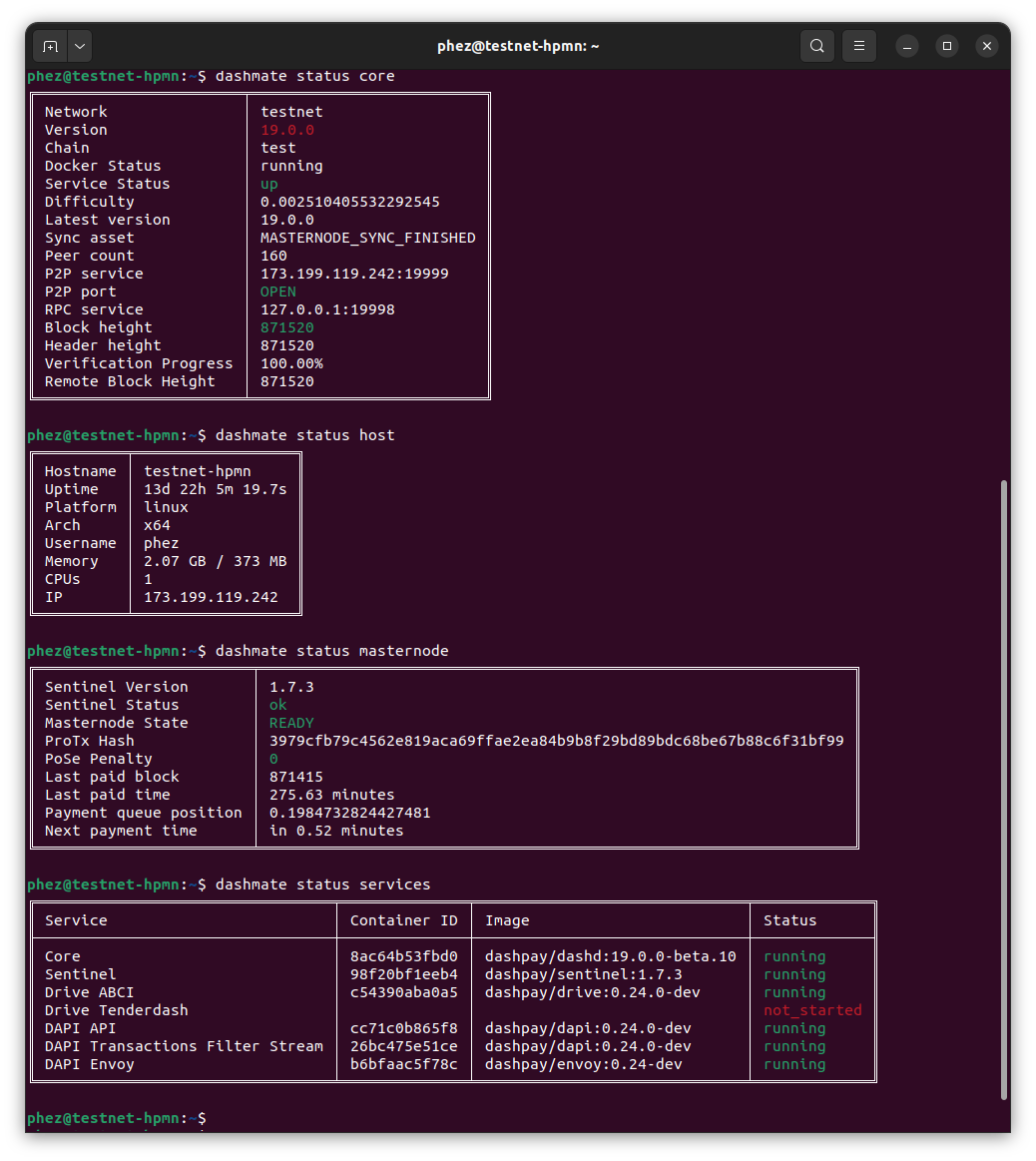
Dashmate displaying a range of status output#
Node update#
You can use dashmate to update minor versions of the software on your
masternode as follows:
dashmate stop
dashmate update
dashmate start
Additional Information#
For further documentation see the dashmate repository.